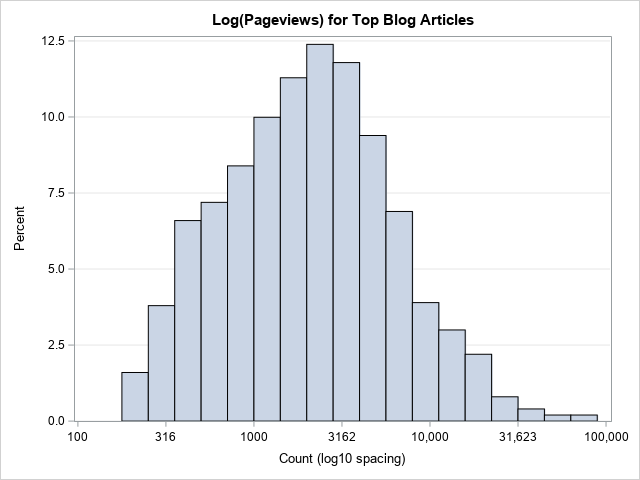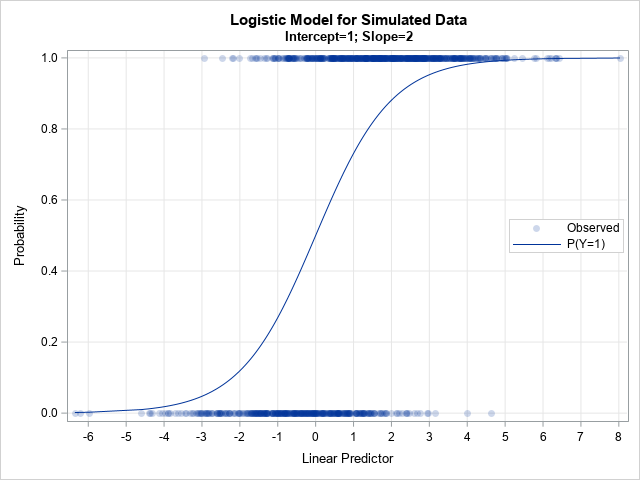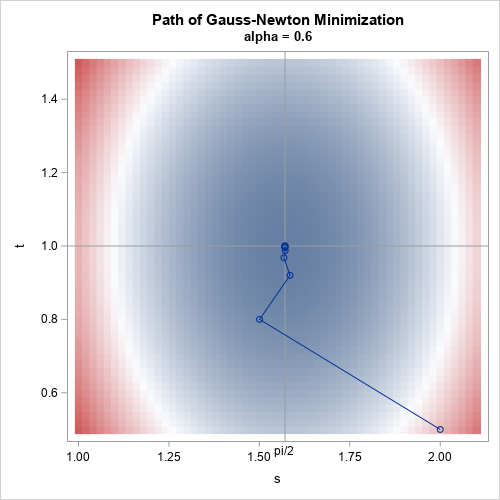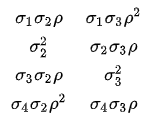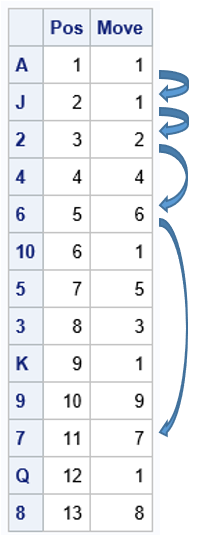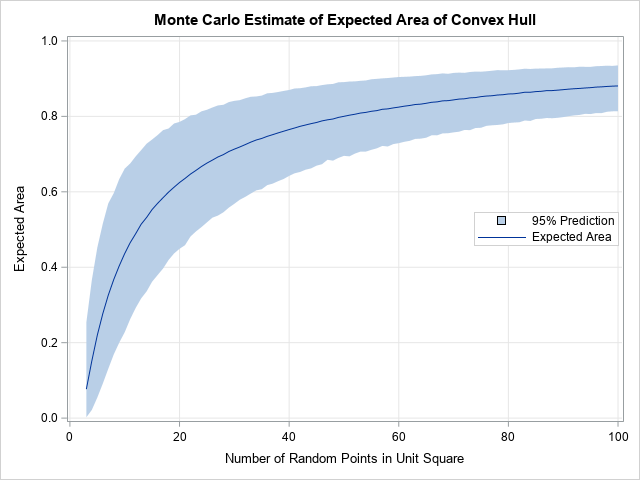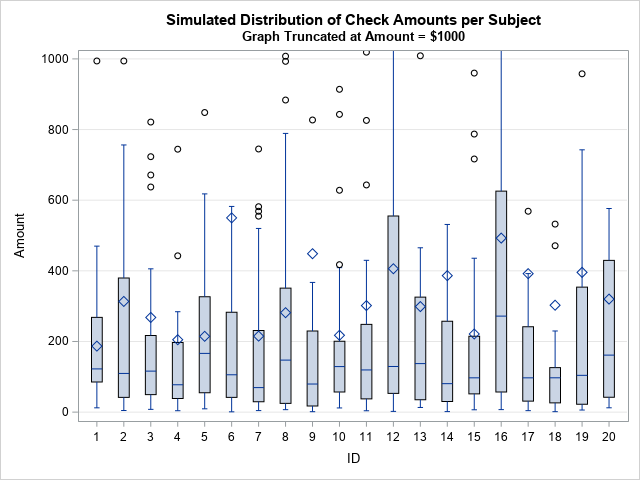
Does anyone write paper checks anymore? According to researchers at the Federal Reserve Bank of Atlanta (Greene, et al., 2020), the use of paper checks has declined 63% among US consumers since the year 2000. The researchers surveyed more than 3,000 consumers in 2017-2018 and discovered that only 7% of