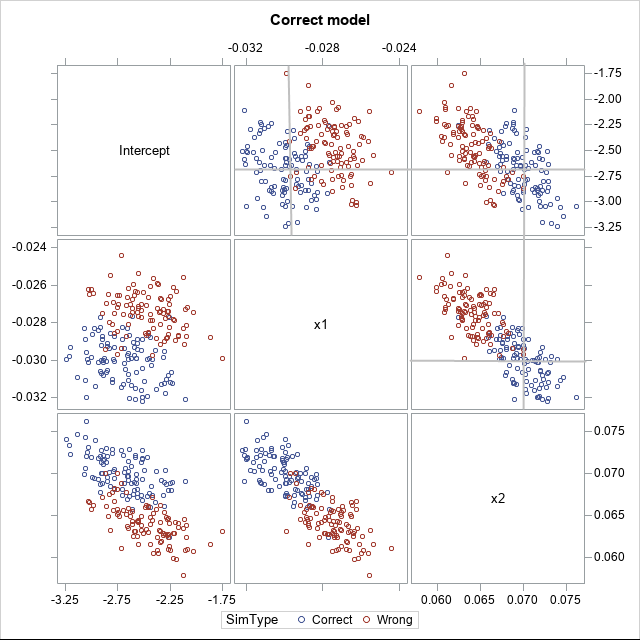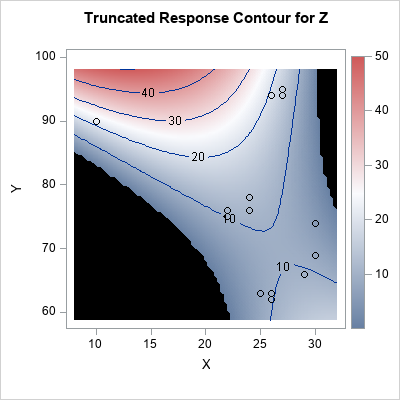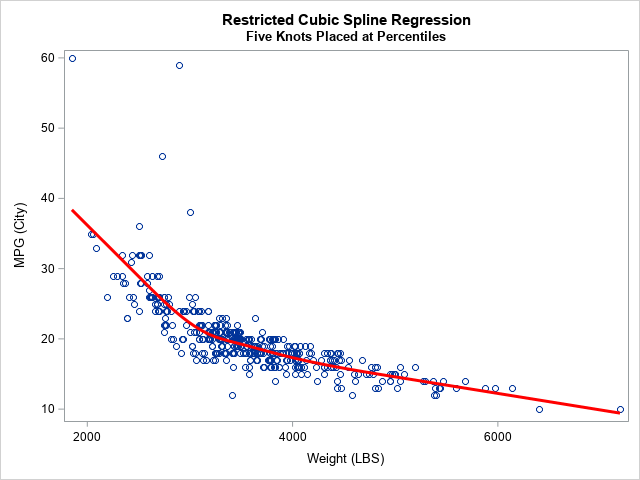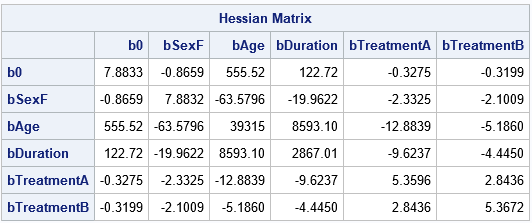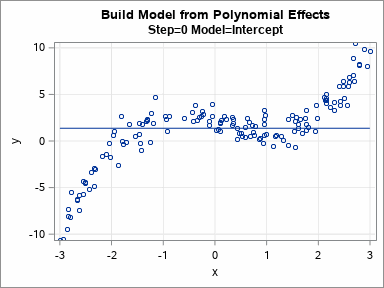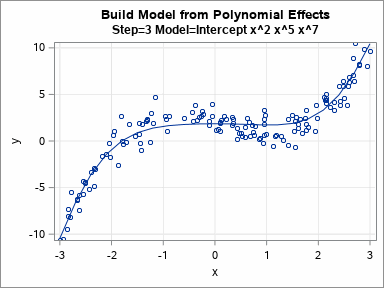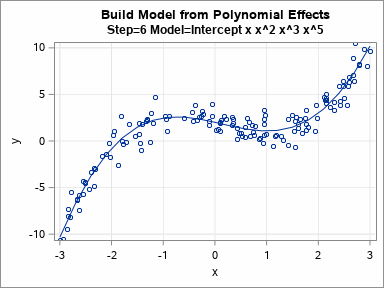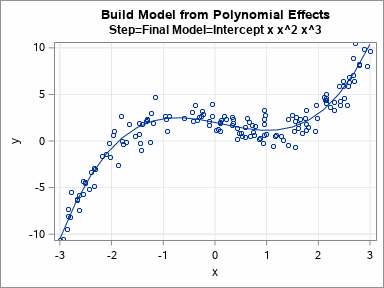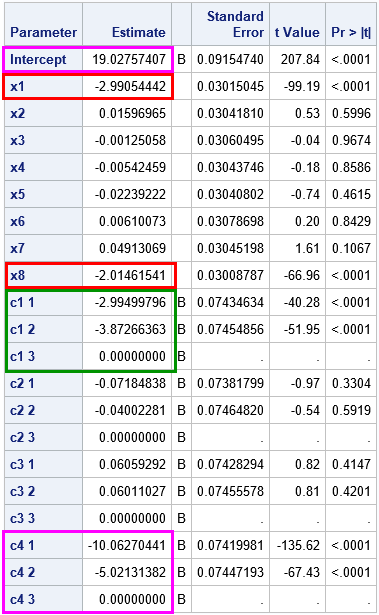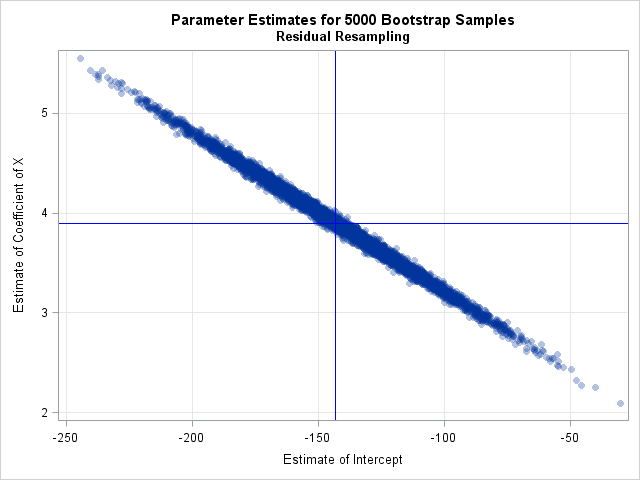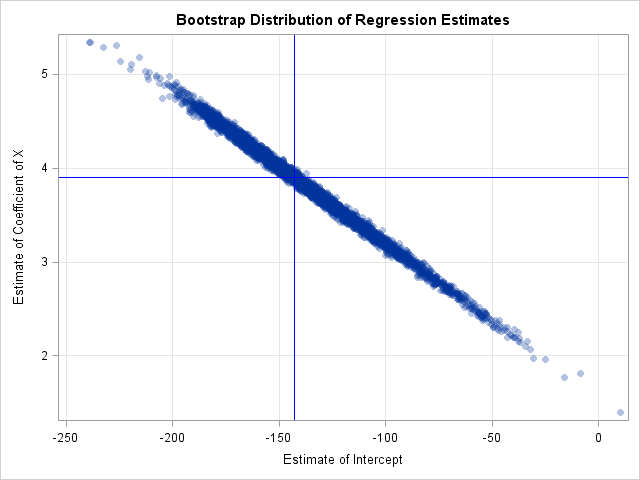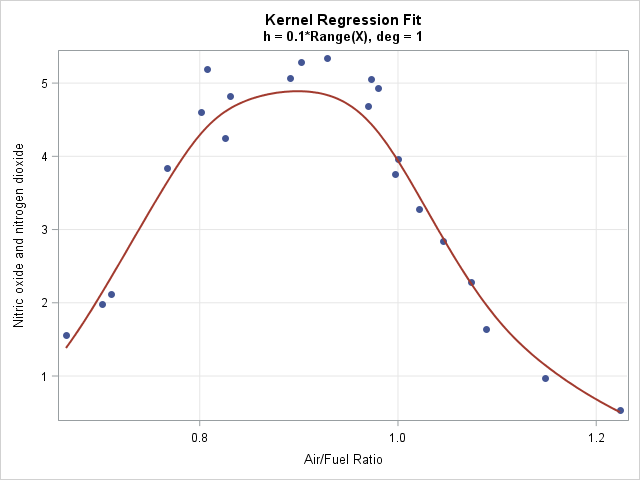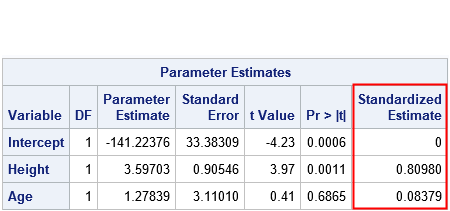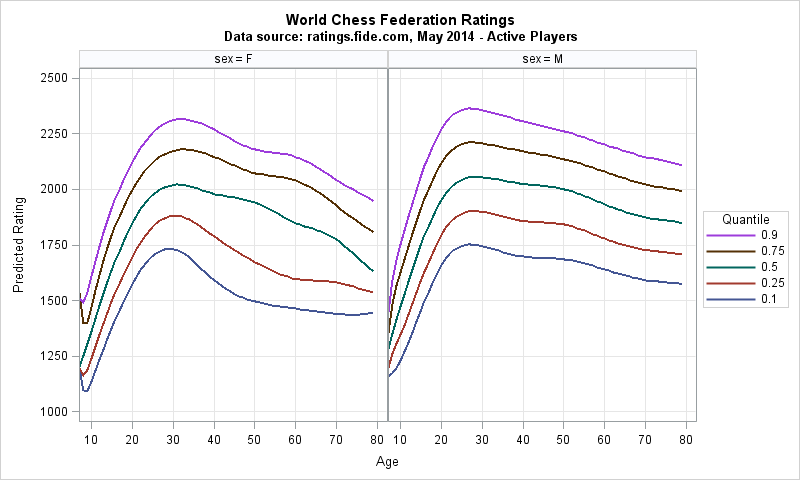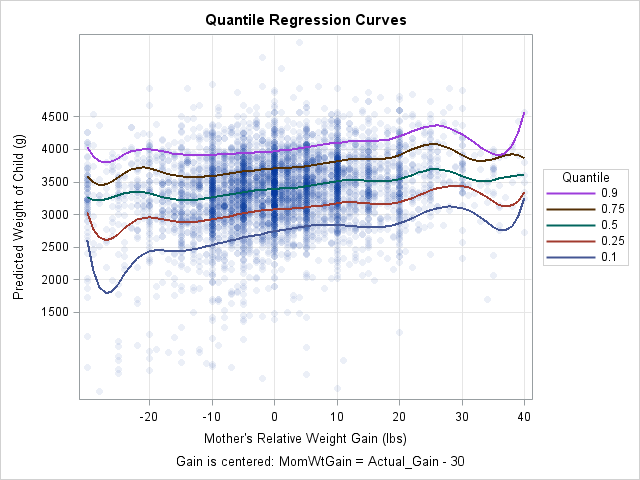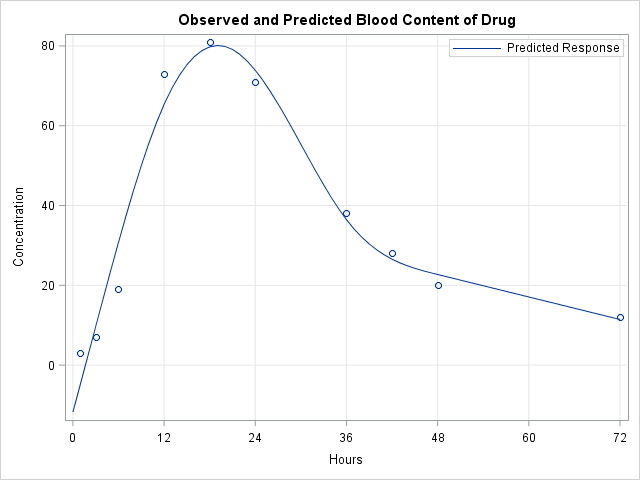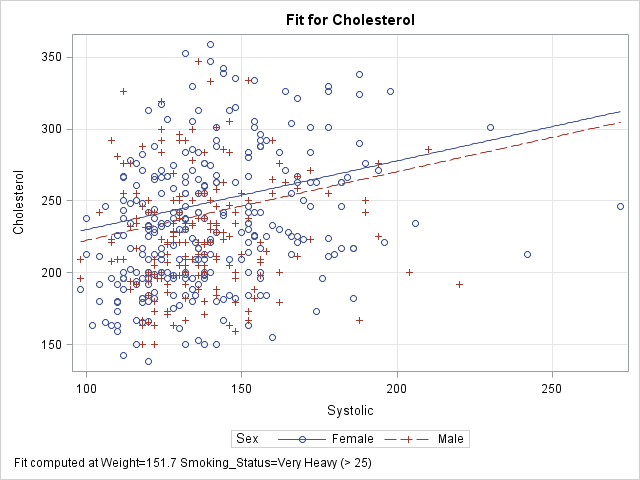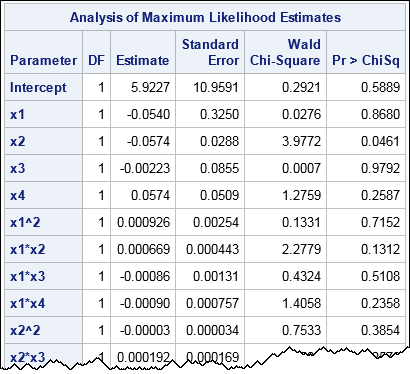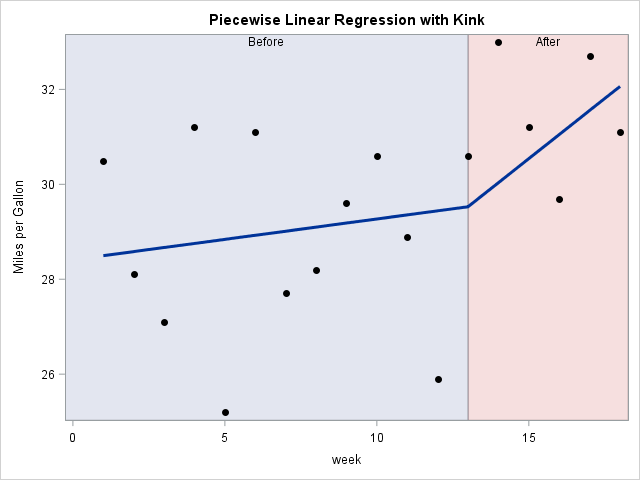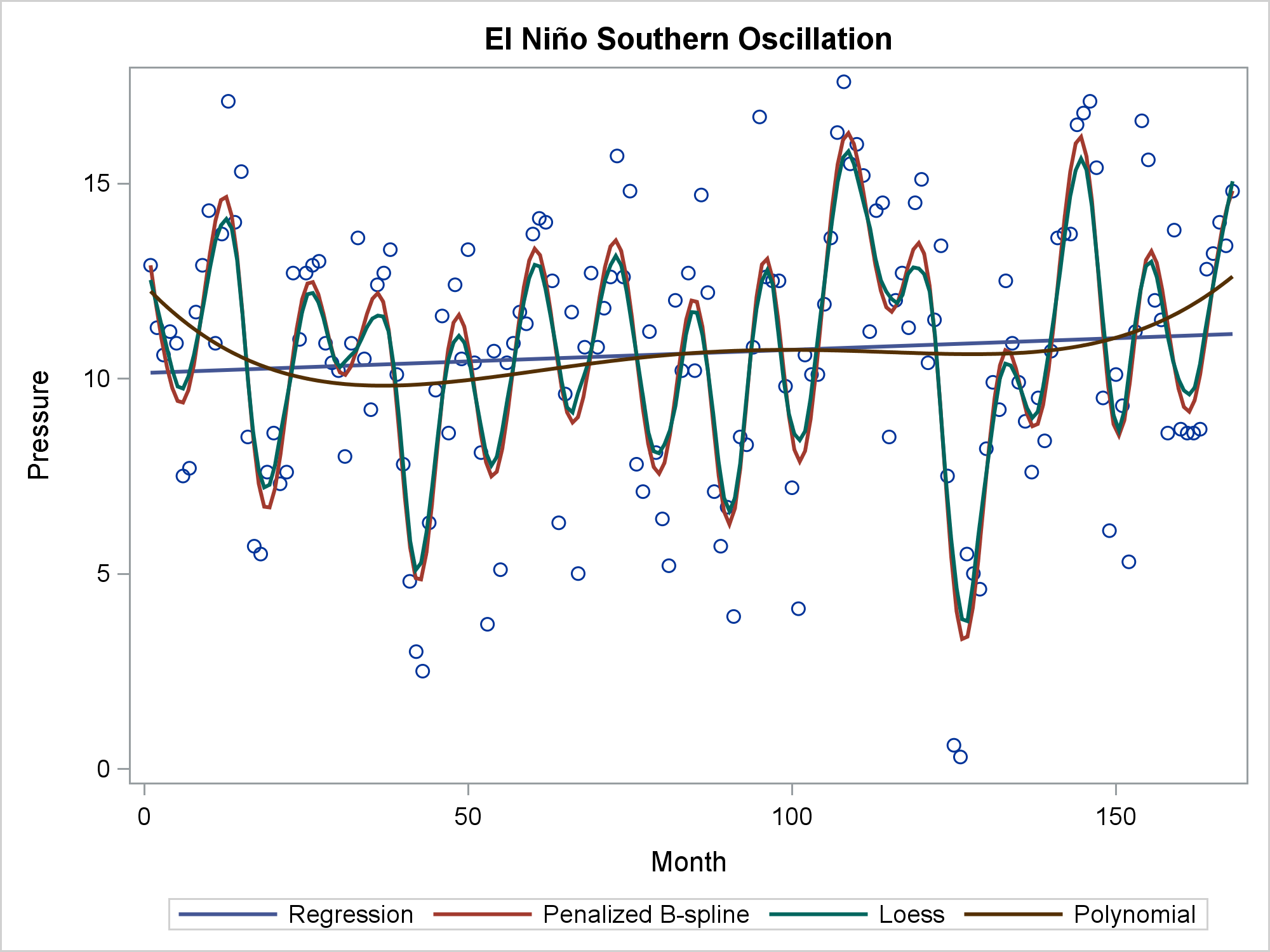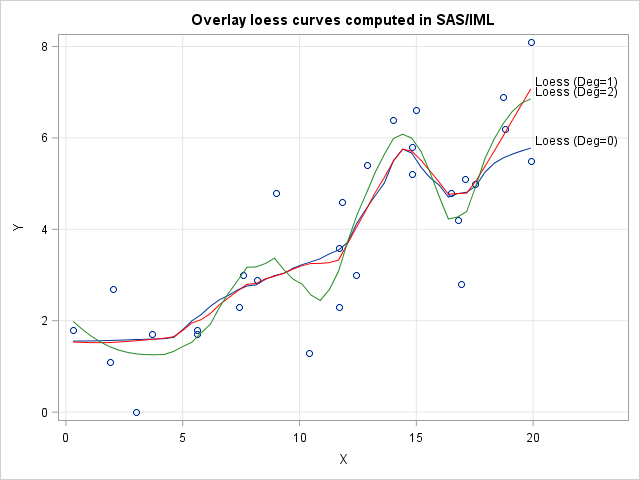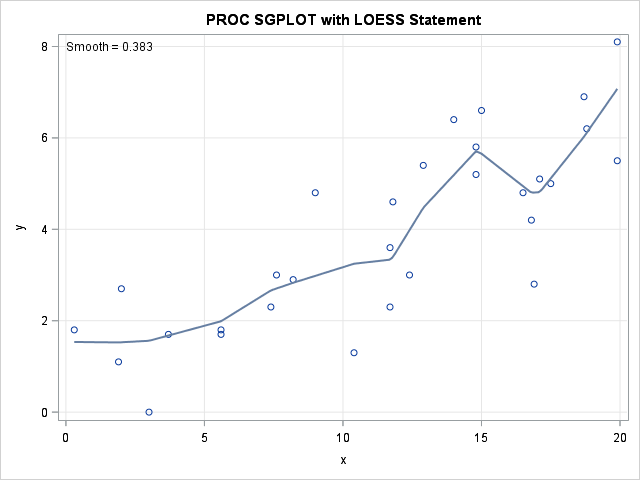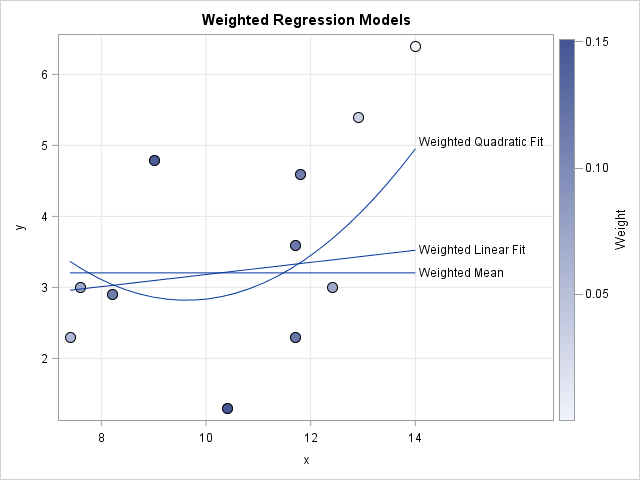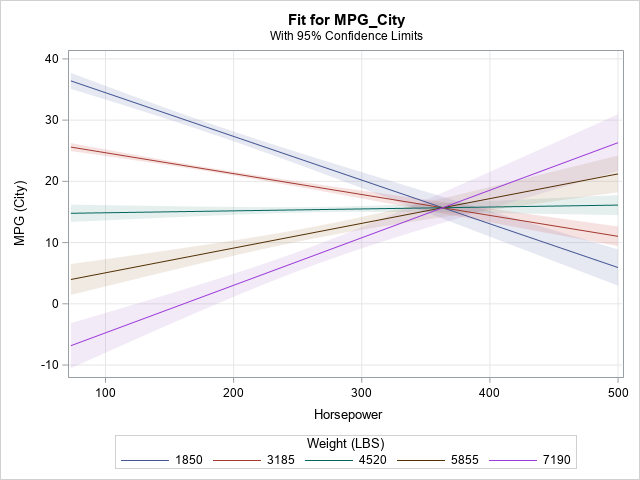
Knowing how to visualize a regression model is a valuable skill. A good visualization can help you to interpret a model and understand how its predictions depend on explanatory factors in the model. Visualization is especially important in understanding interactions between factors. Recently I read about work by Jacob A.