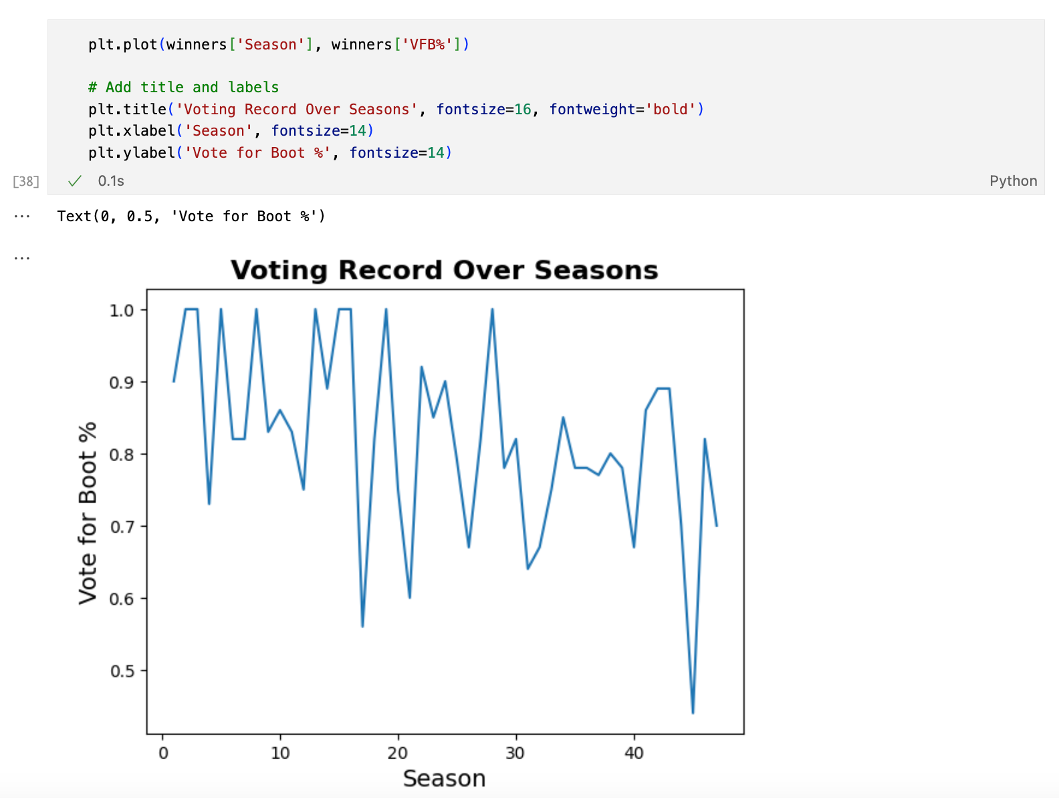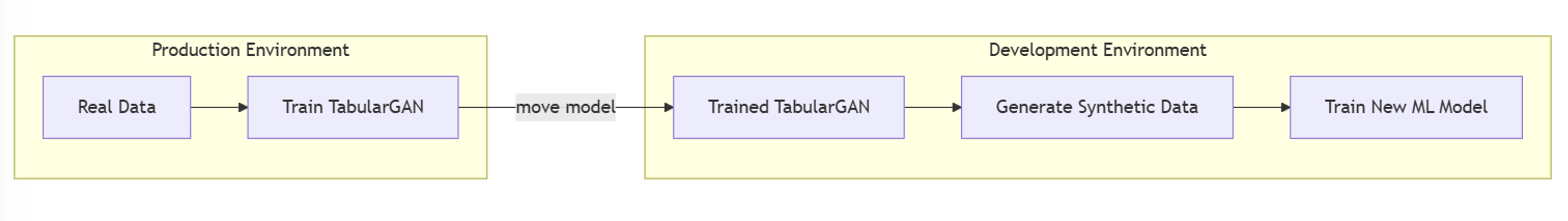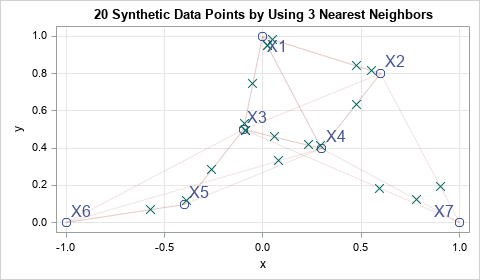
A recent article describes the main features of simulation by using the Synthetic Minority Over-sampling Technique (SMOTE). SMOTE was created to oversample from a set of rare events prior to running a machine learning classification algorithm. However, at its heart, the SMOTE algorithm (Chawla et al., 2002) provides a way