Learn about the latest tips, tutorials, upcoming events and certifications
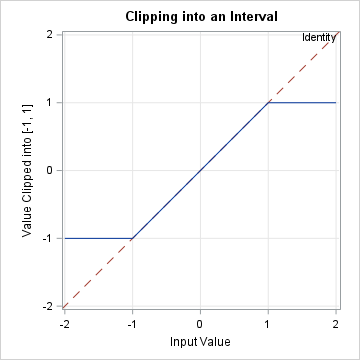
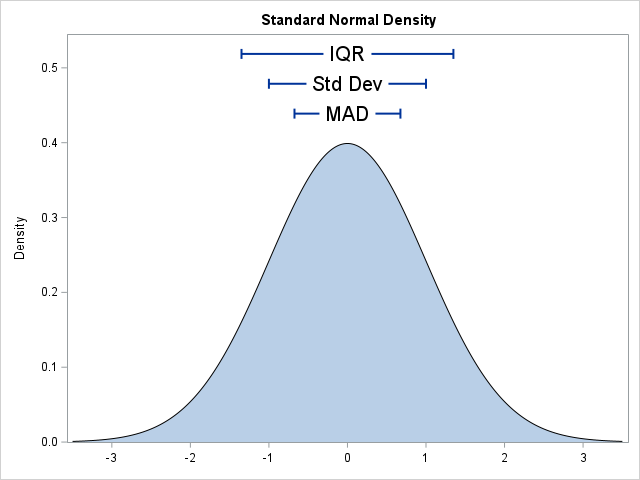
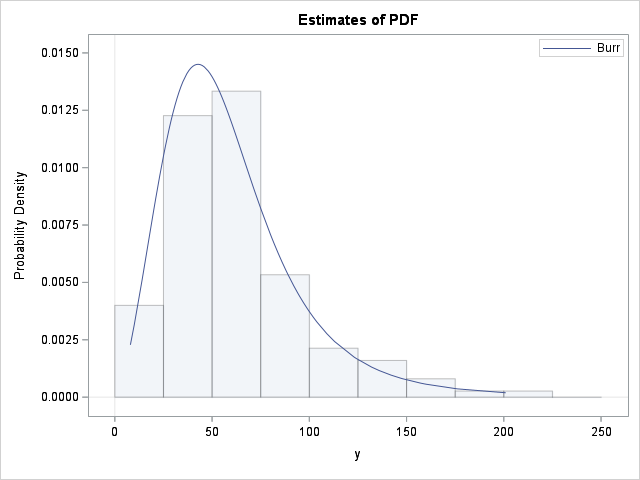
Years ago, I wrote an article about the "trap and cap" programming technique. The idea is that programmers should "trap" inputs to functions (like SQRT, LOG, and QUANTILE functions) to avoid domain errors. In addition, when visualizing a function's range, you should "cap" the output to improve graphs of functions