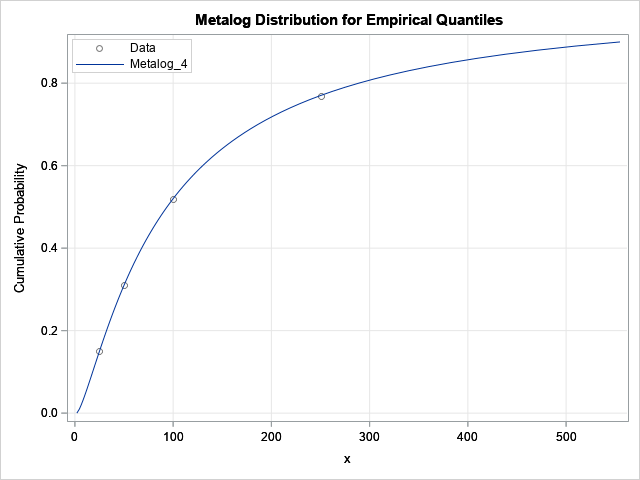
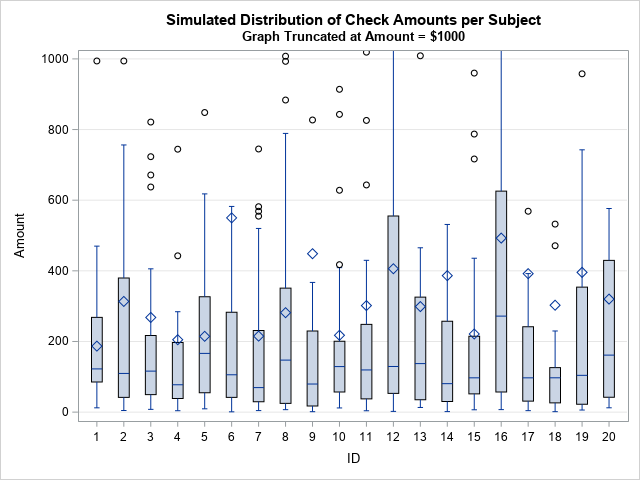
The world’s largest rugby tournament returns for the knockout stages. This blog post explores how probability and simulation can be used to predict likely winners in each of the knockout stages. Team sports are dynamic, time-varying and complex topics to model. When modeling regular competitions, such as domestic leagues, it