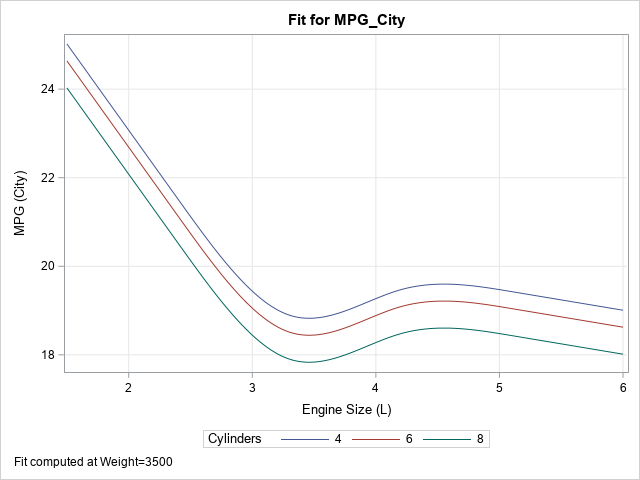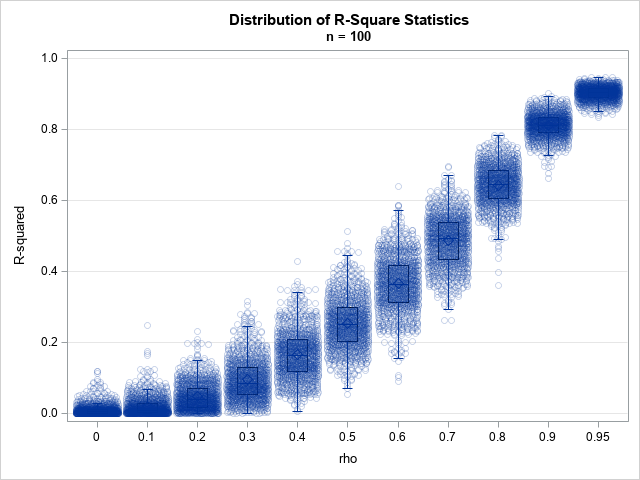
A SAS analyst ran a linear regression model and obtained an R-square statistic for the fit. However, he wanted a confidence interval, so he posted a question to a discussion forum asking how to obtain a confidence interval for the R-square parameter. Someone suggested a formula from a textbook (Cohen,