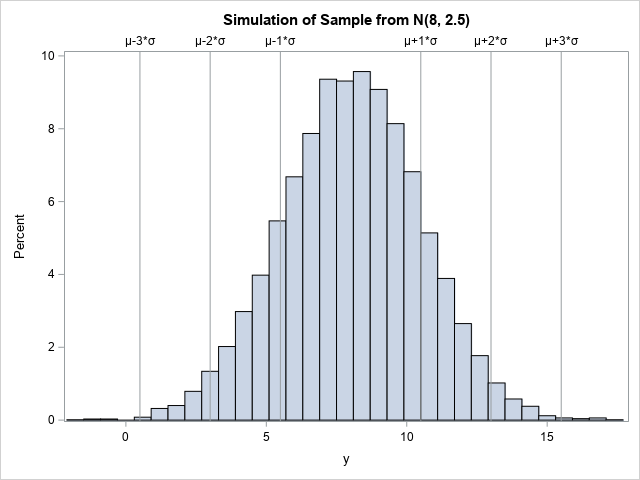
In SAS, the INPUT and PUT functions are powerful functions that enable you to convert data from character type to numeric type and vice versa. They work by applying SAS formats or informats to data. You cannot fully understand the INPUT and PUT functions without understanding formats and informats in