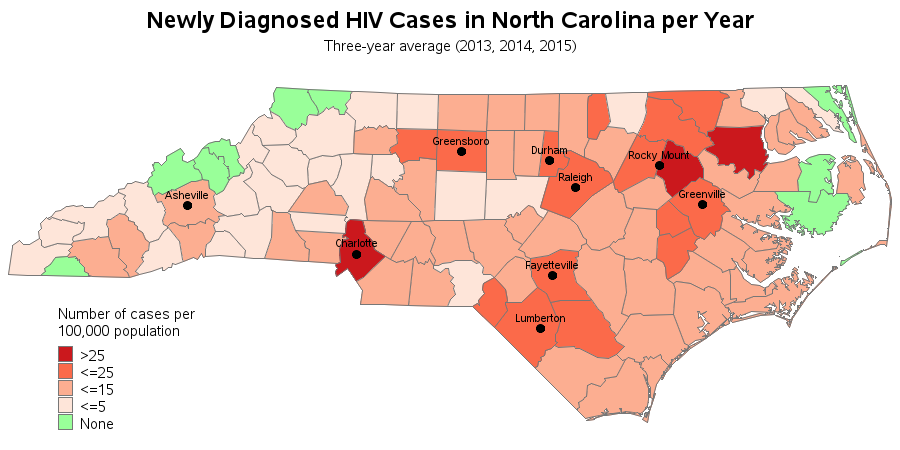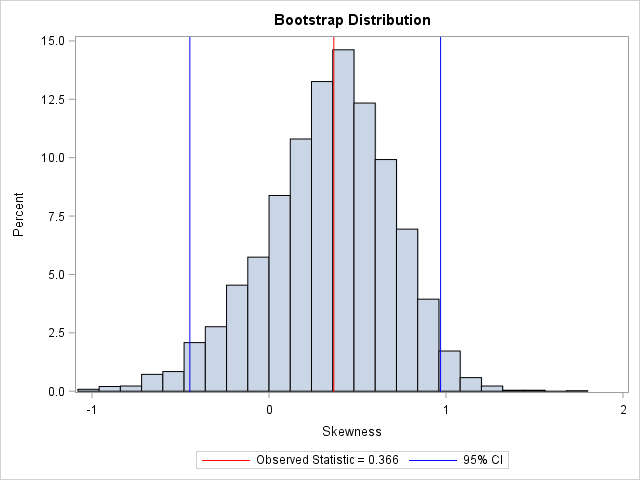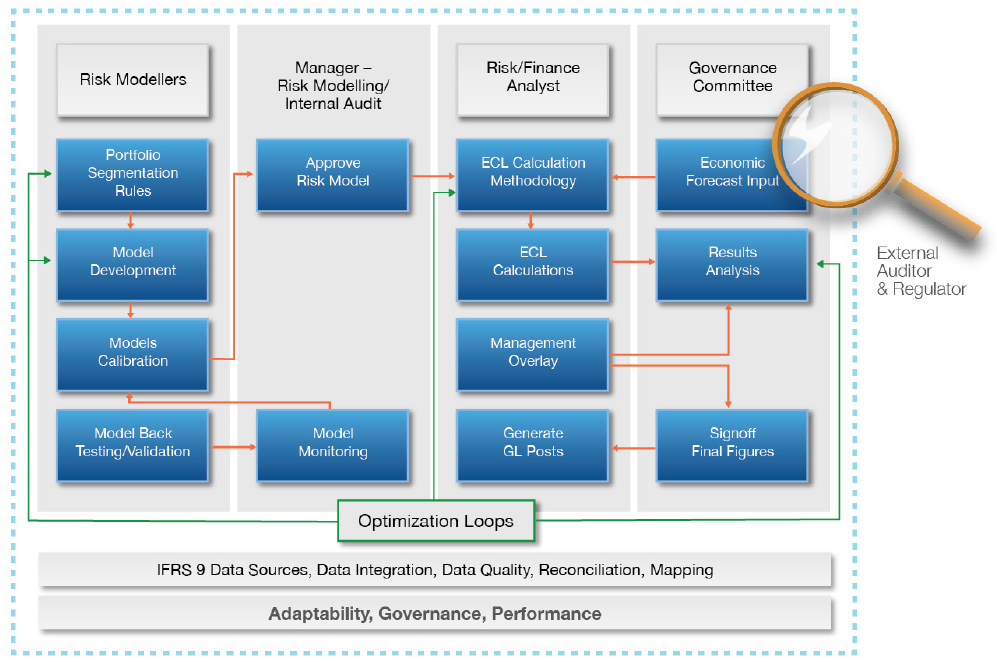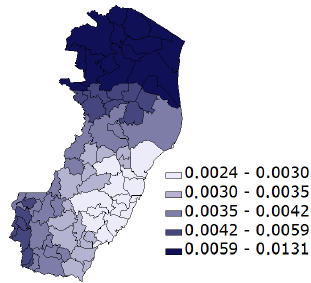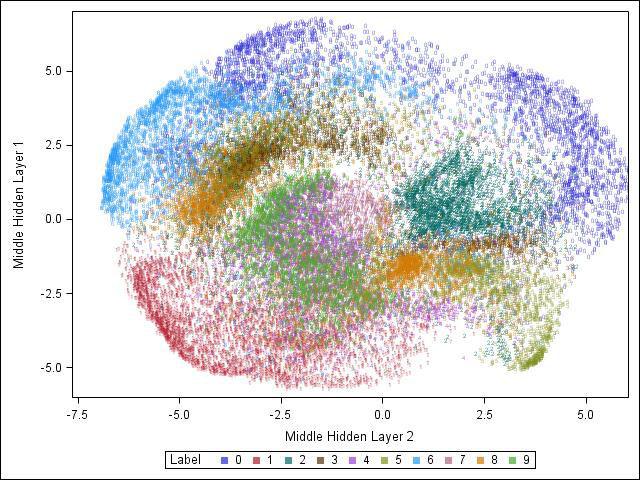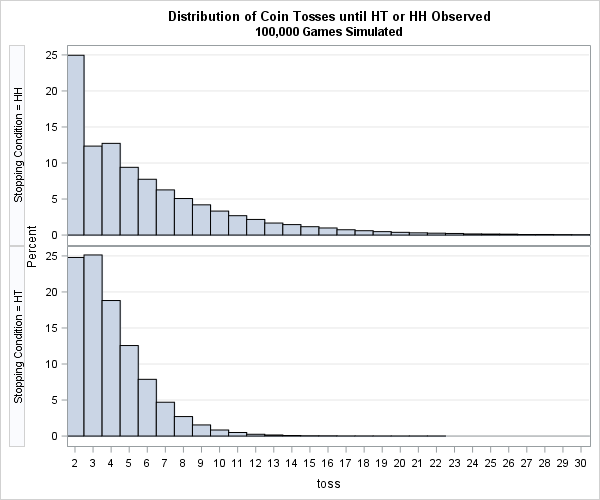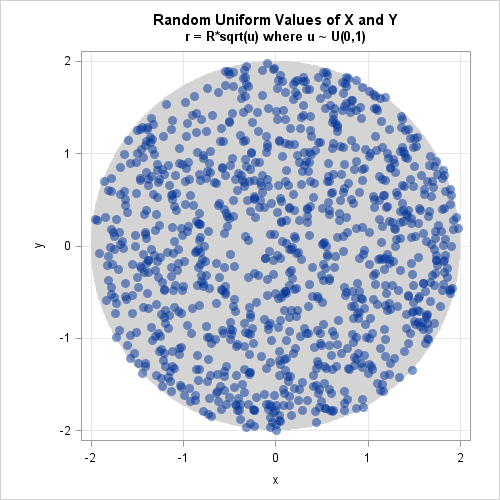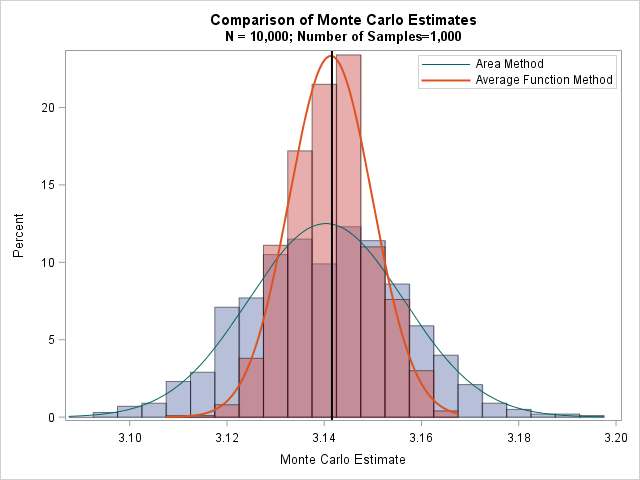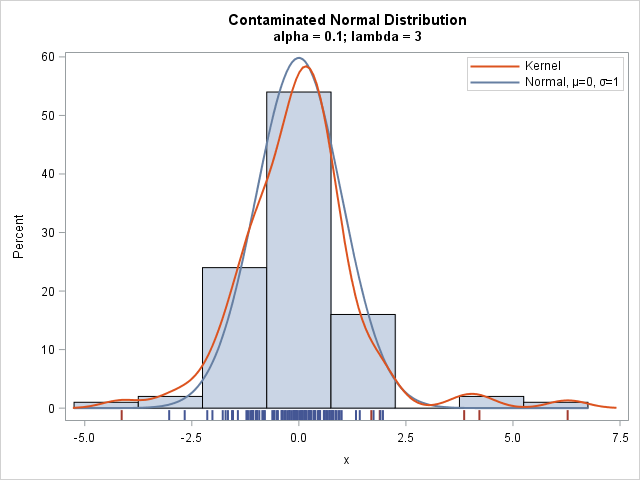
How can you generate data that contains outliers in a simulation study? The contaminated normal distribution is a simple but useful distribution you can use to simulate outliers. The distribution is easy to explain and understand, and it is also easy to implement in SAS. What is a contaminated normal