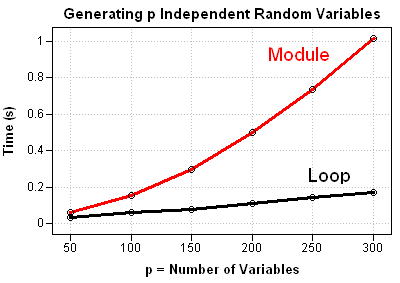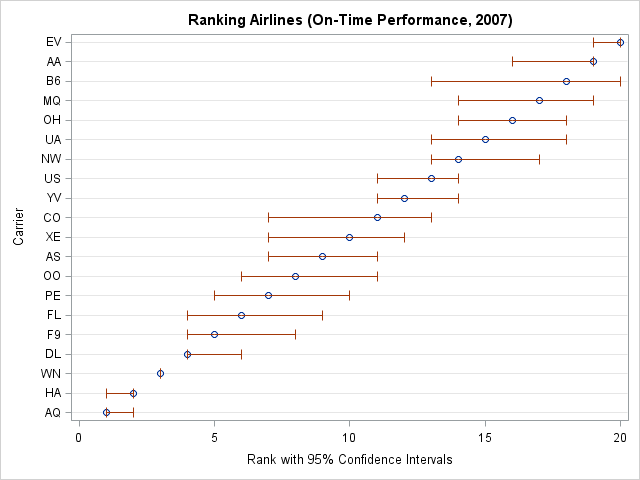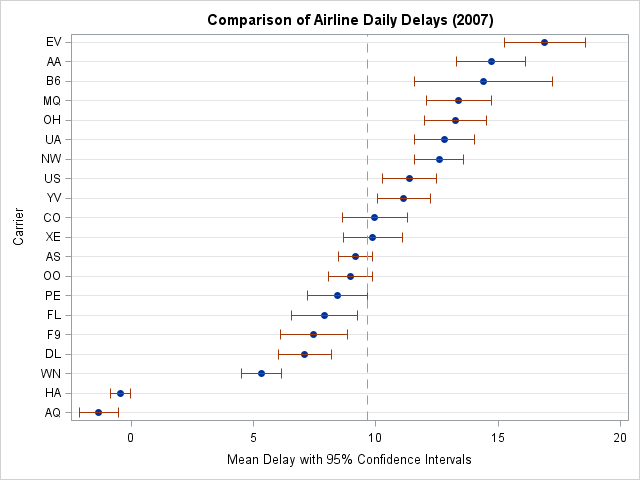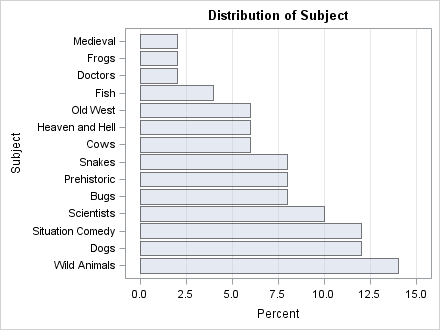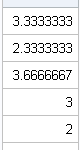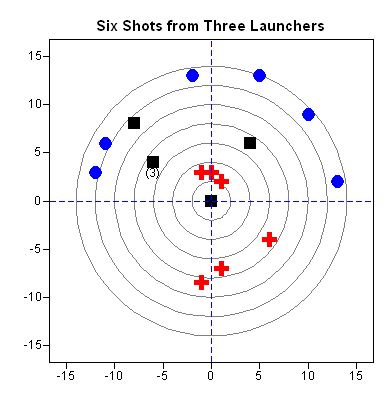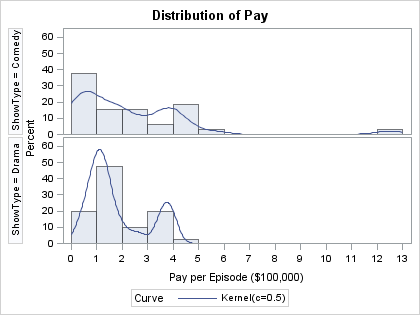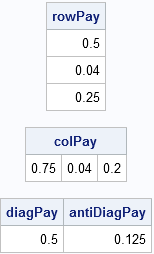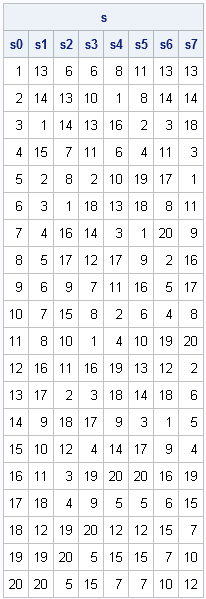
I recently returned from a five-day conference in Las Vegas. On the way there, I finally had time to read a classic statistical paper: Bayer and Diaconis (1992) describes how many shuffles are needed to randomize a deck of cards. Their famous result that it takes seven shuffles to randomize