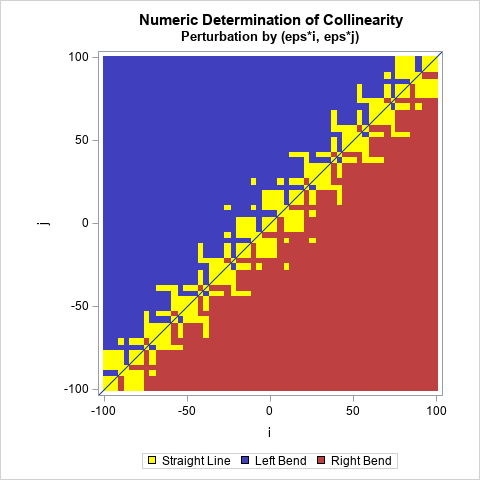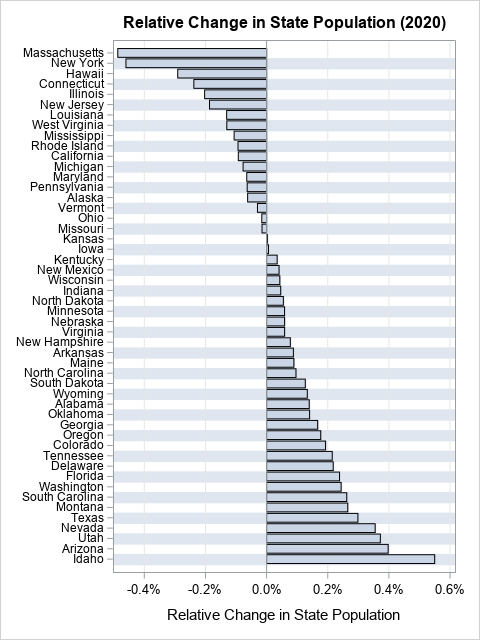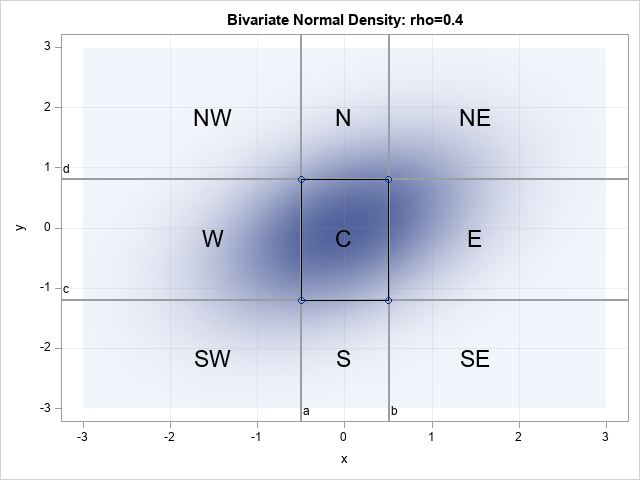
This article shows how to use SAS to compute the probabilities for two correlated normal variables. Specifically, this article shows how to compute the probabilities for rectangular regions in the plane. A second article discusses the computation over infinite regions such as quadrants. If (X,Y) are random variables that are