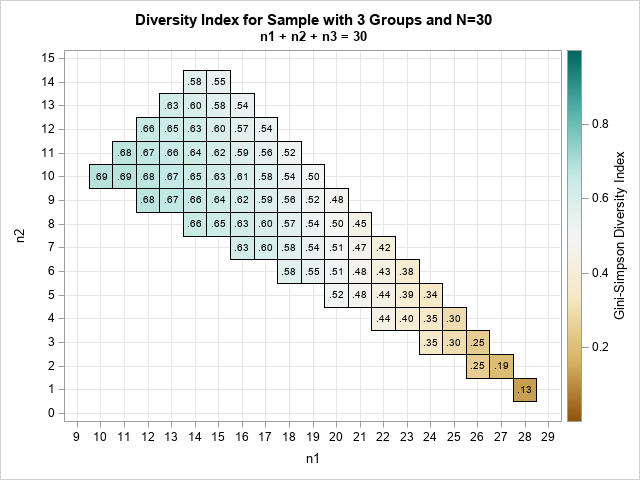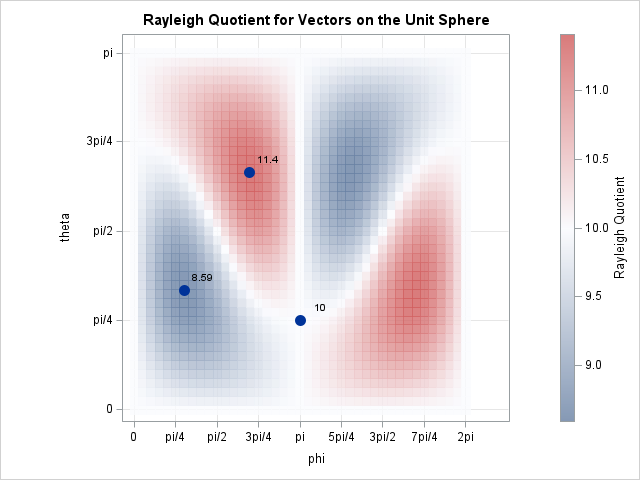
In a previous article, I presented some of the most popular blog posts from The DO Loop in 2025. In general, popular articles deal with elementary topics that have broad appeal. However, I also write technical articles about advanced topics, which typically do not make it onto a Top 10