All Posts

On the Web site for the book Statistical Programming with SAS/IML Software, I provide instructions on how to download the sample data sets and install them so that they can be used from within SAS/IML Studio. When I wrote the book I did not anticipate that SAS users might want
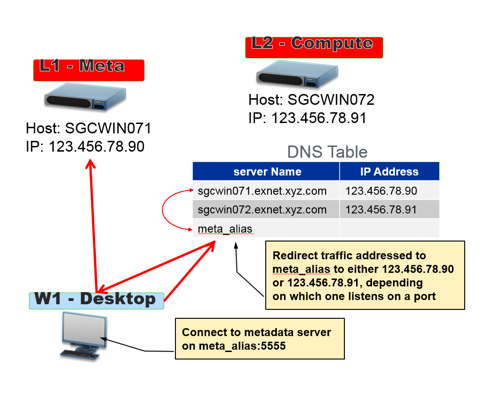
In my last post, I introduced the hardware solutions (such as a virtual IP switch or IP load balancer) that enable client applications to access services regardless of whether they are running on a primary or a failover server in a grid-enabled environment configured with high availability. In this post,

When I work on SAS projects that create lots of files as results, it's often a requirement that those files be organized in a certain folder structure. The exact structure depends on the project, but here's an example: /results |__ html |__ images |__ xls |__ data Before you can
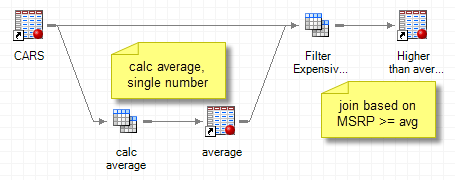
Many SAS Enterprise Guide users practically live in the Query Builder. For those who understand their data tables, the Query Builder provides a tremendous amount of flexibility to pull and manipulate data. The Query Builder produces SQL programs behind the scenes, which translates well for database-centric work. Sometimes a complex

This question comes up often when we’re working with SAS customers to configure their underlying storage arrays: “When is solid-state storage appropriate for SAS applications?” Solid-state drives, or SSDs, are the latest and greatest thing in storage today because they boast extremely fast performance. In this post, I’ll outline how
Recently a user chimed in on the SAS Communities page, requesting a way to add some observation level annotation to a box plot. Wendy was delighted to see a graph created by the UNIVARIATE procedure called "Schematic Plot". In this graph, the box plot of the analysis variable is shown with

Every programmer may dread the thought of a colleague peeking over his or her shoulder, double-checking code, but SAS Global Forum paper winner David Scocca has offered his tips for making code reviews a painless process. His paper, Communicating Standards: A Code Review Experience, is a must-read. Here’s a peek
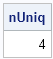
How do you count the number of unique rows in a matrix? The simplest algorithm is to sort the data and then iterate down the rows, comparing each row with the previous row. However, this algorithm has two shortcomings: it physically sorts the data (which means that the original locations
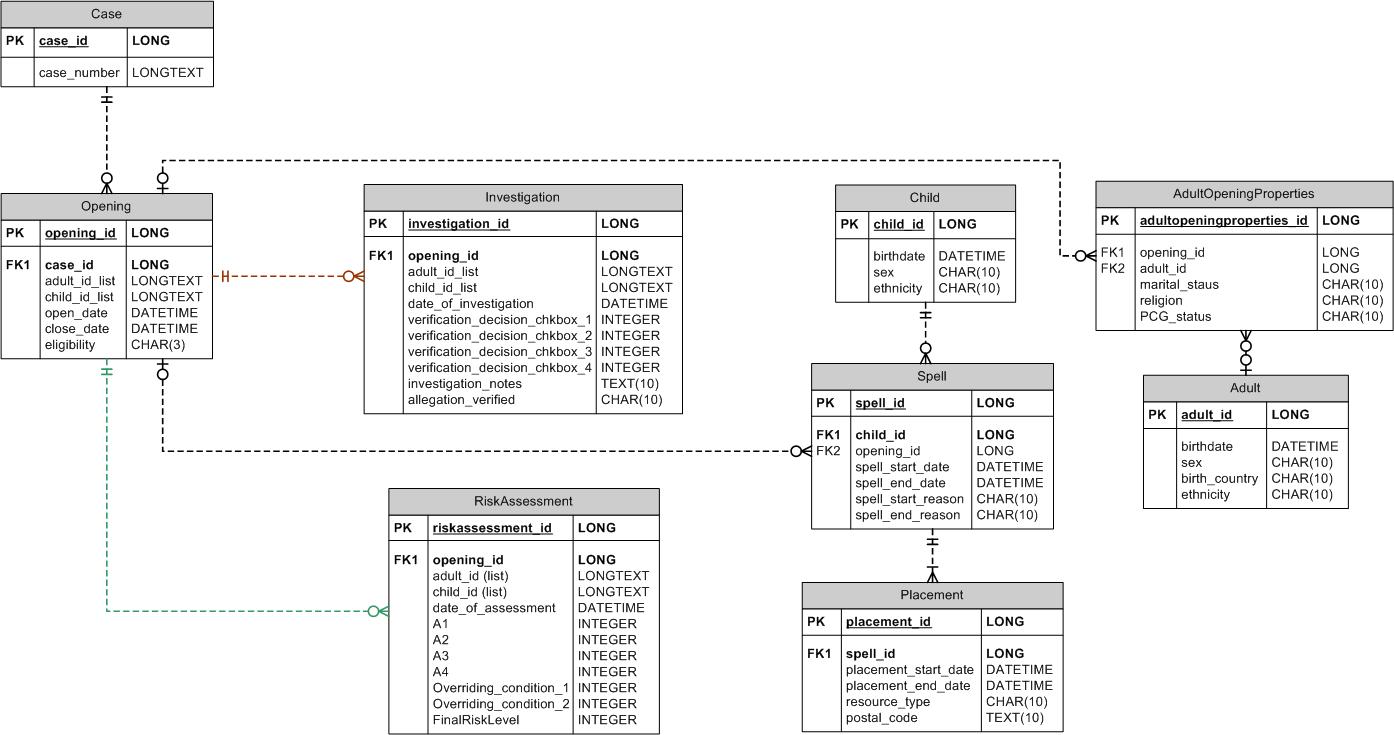
If you routinely import data from external sources, chances are you’ve learned the value in having a systematic import process. In this post, I will begin sharing my approach of using metadata tables to guide the importing of data.

Based on my previous posts, we are almost done with the basics of SAS libraries and how the various clients can access them. Before we leave this topic and go onto third-party database engines, I wanted to spend a few minutes talking about some best practices for making sure that
A Bar Line graph is commonly used in many domains. The SGPLOT procedure makes it easy to create bar line graphs where the user can customize it in many different ways. This post is prompted by a recent question on the communities page on creating such a graph, with one bar and

Most of us can probably recite the age-old recommendation to "drink eight 8-ounce cups of water every day" in our sleep. However, how many of us actually do it? We are often quick to replace our water bottles with sugar-sweetened beverages, coffee, or tea while telling ourselves, "it’s mostly water,

Everyone may find bad dates in their data set from time to time, but it’s often difficult to tell if they’re mere annoyances or indicative of a larger problem. Luckily, Lucheng Shao has come to the rescue in his SAS Global Forum winning paper, Don’t Let a Bad Date Ruin

Imagine a business offering a multitude of products and services that seemingly have little relationship to one another, and all are supported by different data systems. This is the plight of local governments. The products and services produced and managed by local governments range from utilities, solid waste and recycling to parks

This week's SAS tip is from Art Carpenter and his latest book Carpenter's Guide to Innovative SAS Techniques. Art is a talented SAS user and prolific author--and was just recognized in the SAS Circle of Excellence for 30 years of using SAS software. After taking a look at this week's book










