The Swiss army knife is known for its versatility, with a variety of tools and blades to help you complete the task at hand. When you are creating graphics, you sometimes have a special feature you want to add, but you can't seem to find the right syntax "tool" to
Search Results: sgplot (972)
Statistical graphs often include display of derived statistics along with the raw data. Often these statistics are presented in a tabular format inside the graph. With SGPLOT procedure, a table of statistics can be added to the graph as an inset table, as shown below. Using a Stat Table: SGPLOT code:
ODS Graphics components like GTL and SG procedures are designed to work with Styles to create graphs that are effective in the delivery of information and aesthetically pleasing out of the box. You no longer have to tweak the colors to ensure a nice graph. The graph derives all the
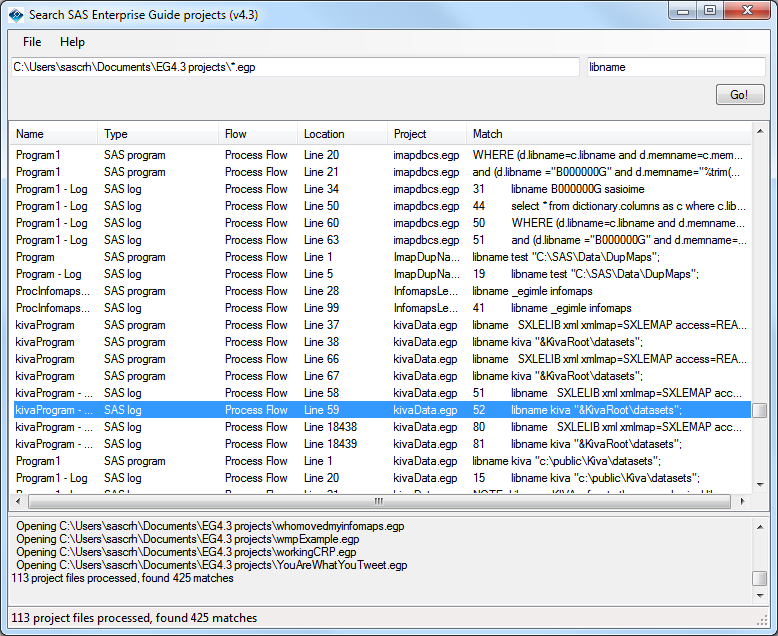
If you are like many SAS Enterprise Guide users, you've amassed a large collection of project files (EGP files) that contain important content: programs, logs, notes, results, and more. However, to most tools and processes, the EGP file is opaque. That is, you can't see what's inside of it unless
A graph in a recent article in Fortune magazine caught my eye. The graph shows the cost of hosting the Summer Olympics over the past eight events. Here is what I termed the "Medal" graph. Now, practitioners of the art of Effective Graphics would likely find some shortcomings in the graph. Clearly

PharmaSUG 2012 conference drew to a close today, concluding two and a half days packed with papers, presentations, posters, hands-on demos and super demos by SAS staff. While the weather outside was a bit chilly from time to time, the conference what hopping with many user papers on how to
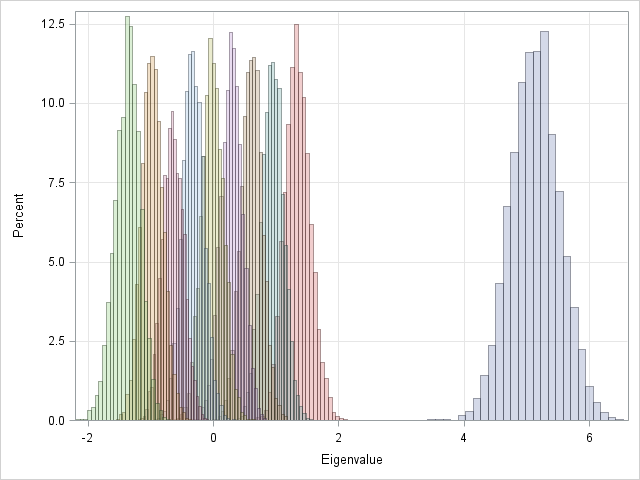
I've been a fan of statistical simulation and other kinds of computer experimentation for many years. For me, simulation is a good way to understand how the world of statistics works, and to formulate and test conjectures. Last week, while investigating the efficiency of the power method for finding dominant
When I was at SAS Global Forum last week, a SAS user asked my advice regarding a SAS/IML program that he wrote. One step of the program was taking too long to run and he wondered if I could suggest a way to speed it up. The long-running step was
Recently I posted an article on this blog on how to create bar charts with log response axes in response to a question by a user. This generated some feedback suggesting that bar charts should not be used with log response axes or with a baseline of anything other than
Getting the axis values just right generally requires some work, and the values you want can change from case to case. One such example was discussed by Dan Heath in his post on custom axis values. Here Dan shows the usage of non uniform axis values using the VALUES option on
Creating bar charts with log response axis has come up a few times in the past few days. Before we look into how we could do this, it would be worth pointing out the considerable opinion in the blogosphere against use of log response axes for bar charts. See BizIntelGuru and
On Friday before the conference, I presented a 1 day "developer led" seminar on SG Procedures and GTL, along with a discussion of new features for SAS 9.3. The experience was very gratifying as all users were now using SAS 9.2, and some were using SAS 9.3. We had a lively
Recently, a user asked about creating a Bar Chart of Value by Date, where the dates are displayed on a scaled interval axis. Consider this simulated data set of value by date and treatment shown below. This data set only has one value for each date and treatment combination. We can use the VBAR statement
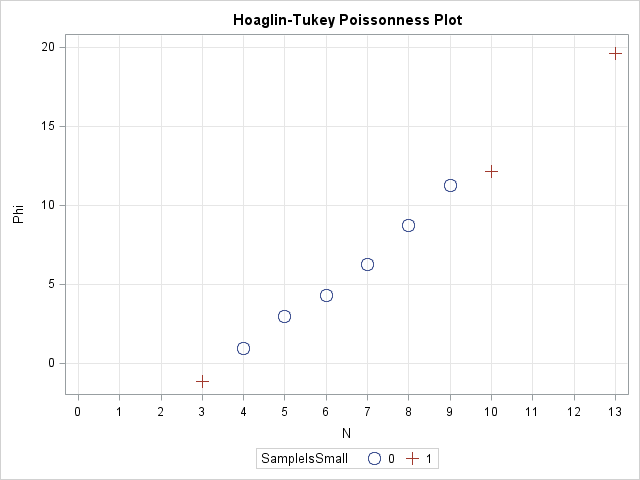
Last week I discussed how to fit a Poisson distribution to data. The technique, which involves using the GENMOD procedure, produces a table of some goodness-of-fit statistics, but I find it useful to also produce a graph that indicates the goodness of fit. For continuous distributions, the quantile-quantile (Q-Q) plot
A recent article in the SAS and R blog was about current winter temperatures in Albany, NY. The temperature data for the recent winter (Dec 2011 - Mar 2012) was plotted on a polar graph. Robert Allison posted an article on displaying the same data as a Polar Graph using SAS/GRAPH . Here is his
The birthday matching problem is a classic problem in probability theory. The part of it that people tend to remember is that in a room of 23 people, there is greater than 50% chance that two people in the room share a birthday. But the birthday matching problem is also
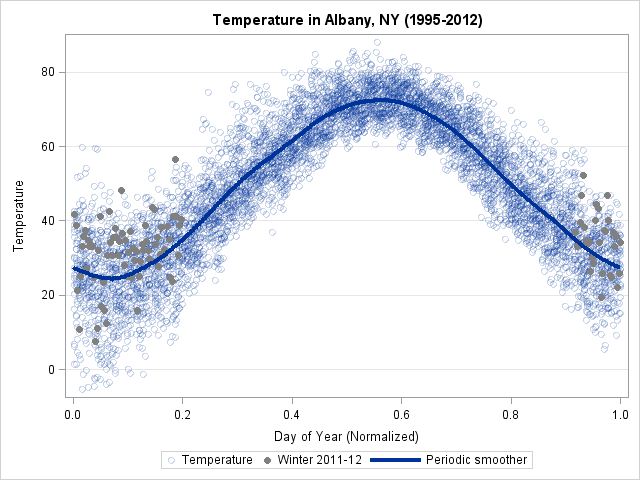
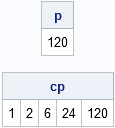
In yesterday's post, I discussed a "quick and dirty" method to smooth periodic data. However, after I smoothed the data I remarked that the smoother itself was not exactly periodic. At the end points of the periodic interval, the smoother did not have equal slopes and the method does not
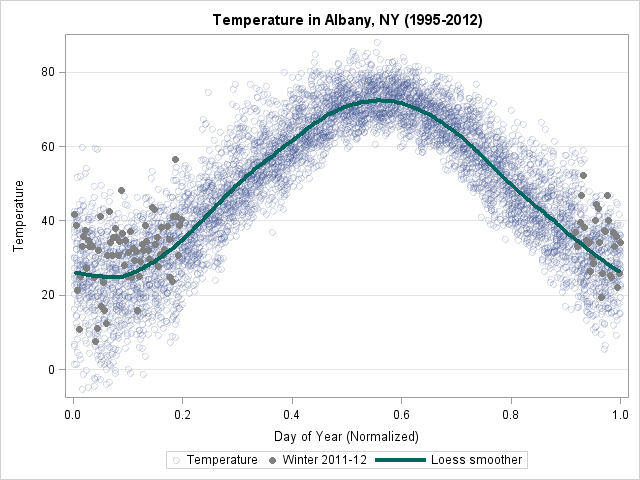
Over at the SAS and R blog, Ken Kleinman discussed using polar coordinates to plot time series data for multiple years. The time series plot was reproduced in SAS by my colleague Robert Allison. The idea of plotting periodic data on a circle is not new. In fact it goes
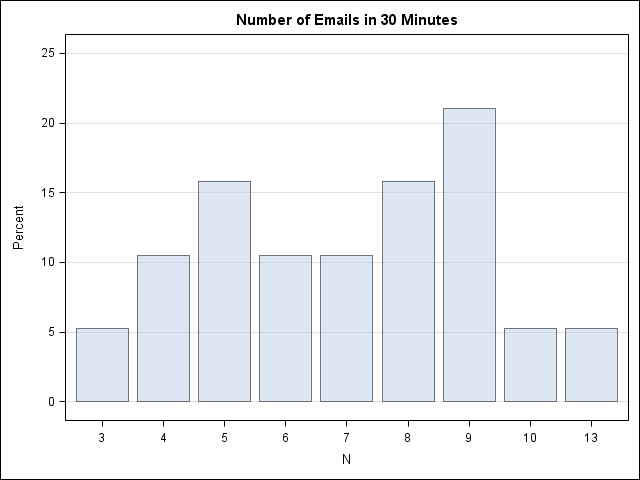
Over at the SAS Discussion Forums, someone asked how to use SAS to fit a Poisson distribution to data. The questioner asked how to fit the distribution but also how to overlay the fitted density on the data and to create a quantile-quantile (Q-Q) plot. The questioner mentioned that the
A user recently posted a question in the SAS communities forum about how to best display two measures by one classifier using a Bar-Line graph, where the scale of the two measures is vastly different. This got me thinking about various different ways to represent such data. Here are some of my thoughts,
The topic of cluster groups comes up often. By cluster group I am referring to the feature in bar charts where the group values are displayed side by side. With SAS 9.3, SG Procedures support stack or cluster grouping for Bar Charts and overlay or cluster grouping for all other
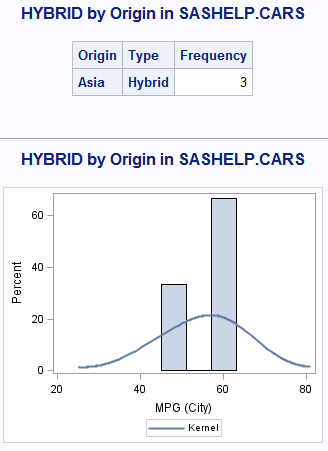
How to write a SAS macro program to repeat your SAS processing for each value of a BY grouping variable.
When the data is classified by multiple class variables, you can certainly create graphs using BY variables. This results in separate graphs, one for each level of the BY variable crossings. Each graph is scaled by its own data subset, and comparisons across BY levels is harder. When comparisons need to be
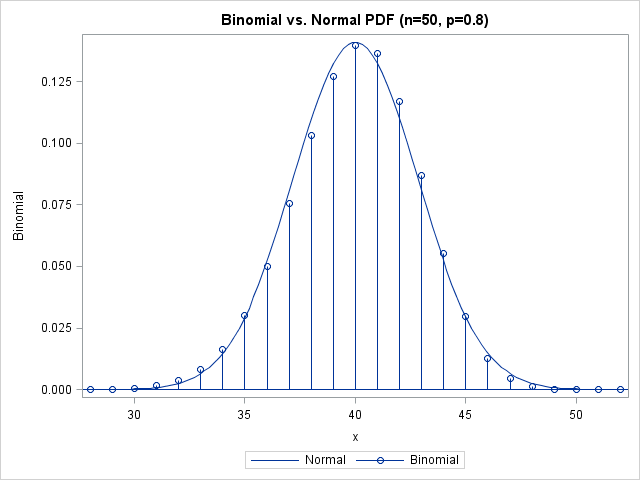
Most statistical programmers have seen a graph of a normal distribution that approximates a binomial distribution. The figure is often accompanied by a statement that gives guidelines for when the approximation is valid. For example, if the binomial distribution describes an experiment with n trials and the probability of success
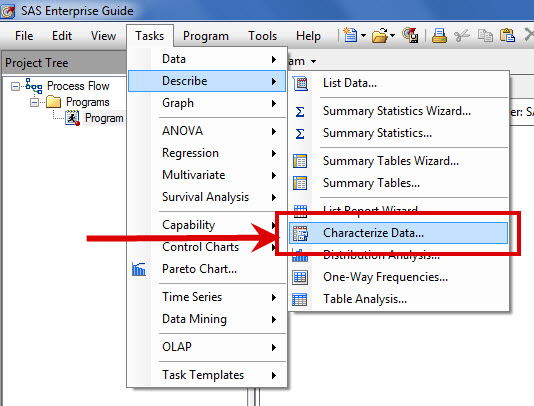
During IFSUG yesterday, Sunil Gupta gave attendees to his presentation a special homework assignment. Look into the SAS Enterprise Guide task 'Characterize Data'. Sunil suggested that this was a simple approach to quickly getting a summary of all the variables within your data table. Of course, some programmers will use
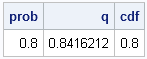
I work with continuous distributions more often than with discrete distributions. Consequently, I am used to thinking of the quantile function as being an inverse cumulative distribution function (CDF). (These functions are described in my article, "Four essential functions for statistical programmers.") For discrete distributions, they are not. To quote
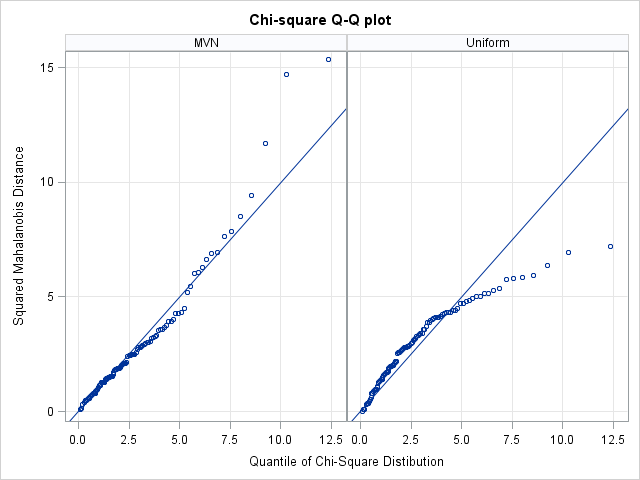
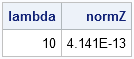
I've blogged several times about multivariate normality, including how to generate random values from a multivariate normal distribution. But given a set of multivariate data, how can you determine if it is likely to have come from a multivariate normal distribution? The answer, of course, is to run a goodness-of-fit
This classic start to a romantic poem assumes that the correct colors are always assigned to the correct flowers; but, for those who create graphs for reports, consistent color assignment can be more of a challenge than an assumption. This challenge is particularly true for the display of group values.
The graph showing the distribution of the maximum liver function test values by treatment for all participants in a study is commonly used for the analysis of safety data in clinical trials. The data is often structured in multiple columns (one per treatment) as below on the left, or grouped by
Here is the second installment of sample graphs from the SG Procedures book - The Adverse Event Timeline. This is a graph commonly used in patient profiles for clinical trials where we track the progress of a patient through a hospitalization event, tracking the dates and severity of the adverse events. The





