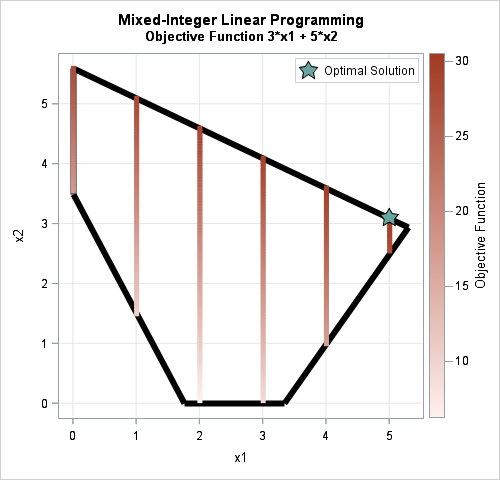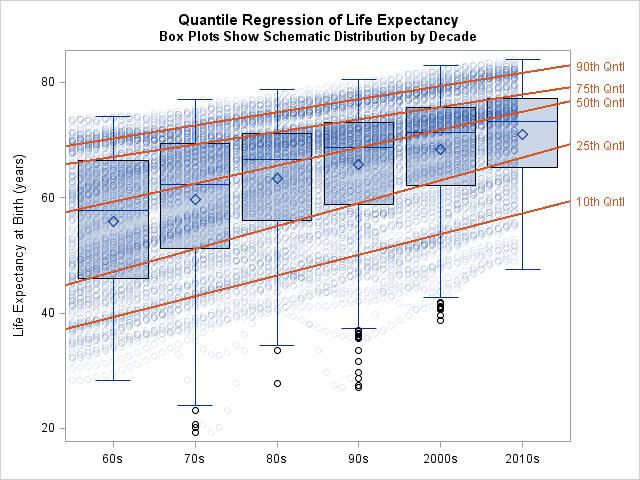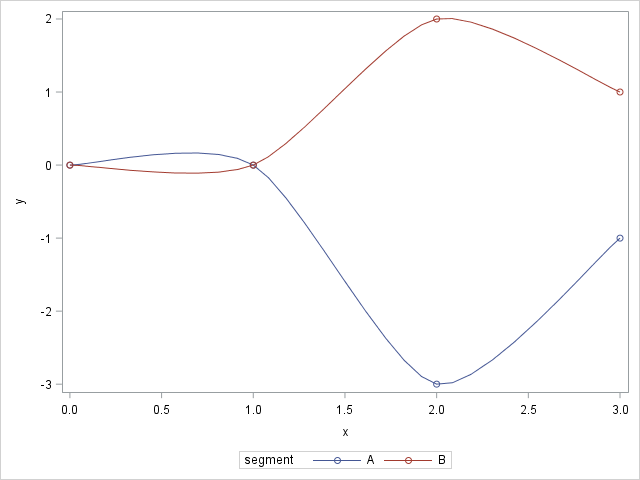
By default, when you use the SERIES statement in PROC SGPLOT to create a line plot, the observations are connected (in order) by straight line segments. However, SAS 9.4m1 introduced the SMOOTHCONNECT option which, as the name implies, uses a smooth curve to connect the observations. In Sanjay Matange's blog,