SAS Users
Providing technical tips and support information, written for and by SAS users.
Getting Started with Python Integration to SAS® Viya® - Part 7 - Filtering CAS Tables
Welcome to the seventh installment in my series Getting Started with Python Integration to SAS Viya. In previous posts, I discussed how to connect to the CAS server, how to execute CAS actions, and how to work with the results. Now it's time to learn how to filter CAS tables. Load and explore data

Automating Excel workbooks creation using SAS
Leonid Batkhan shows you how to automate and improve a sometimes onerous hands-on process of creating Excel workbooks.
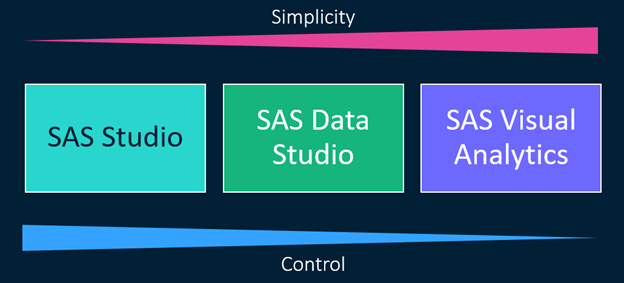
Beggars can’t be choosers…Unless they’re using SAS Viya
Have you ever heard the phrase “beggars can’t be choosers”? Basically, it means that if you ask for something, be grateful for what you get, especially if you don’t have the means to acquire it yourself. This phrase can be widely applicable to most areas of our lives, but when


