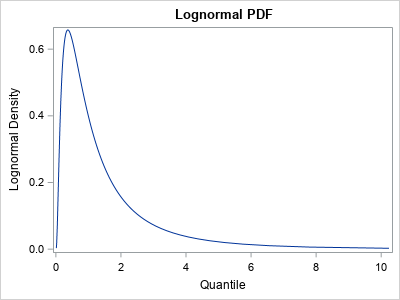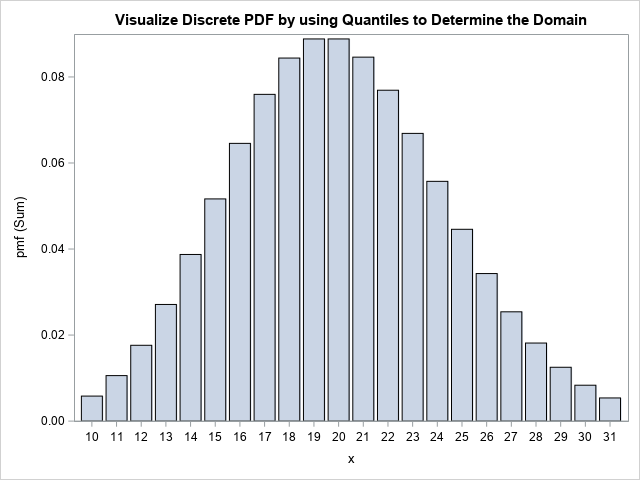
It isn't easy to draw the graph of a function when you don't know what the graph looks like. To draw the graph by using a computer, you need to know the domain of the function for the graph: the minimum value (xMin) and the maximum value (xMax) for plotting