SAS Users
Providing technical tips and support information, written for and by SAS users.
Getting Started with Python Integration to SAS Viya for Predictive Modeling - Imputing Missing Values
In part 1 of this series, we examined our data before building any models. Among the discoveries were missing values in some of our columns. Missing values are an inevitable part of data analysis. Whether it's due to a faulty sensor, human error, or simply the absence of information, missing
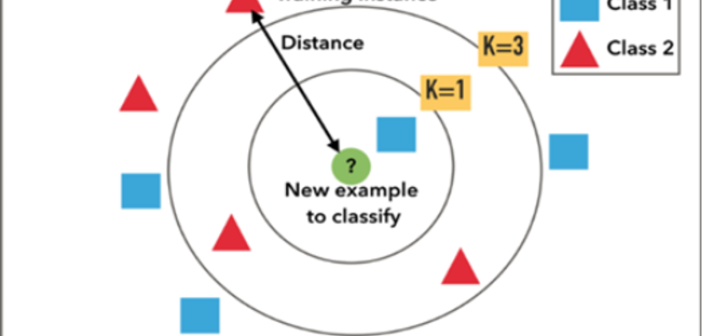
Using K Nearest Neighbours algorithm in scenario tuning
K Nearest Neighbour is an algorithm that stores all the available observations and classifies the new data based on a similarity measure.

Extract text from a PDF file using SAS Viya
You most likely have used a Portable Document Format (PDF) file in one form or another. Now, what if you have a PDF file and want to extract the text from the file? What if the PDF file contains input fields that a user fills in and you want to


