The DO Loop
Statistical programming in SAS with an emphasis on SAS/IML programs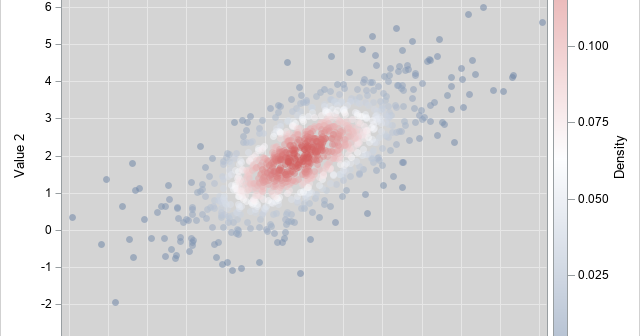
A previous article shows how to compute the probability density function (PDF) for the multivariate normal distribution. In a similar way, you can compute the density function for the multivariate t distribution. This article discusses the density function for the multivariate t distribution, shows how to compute it, and visualizes
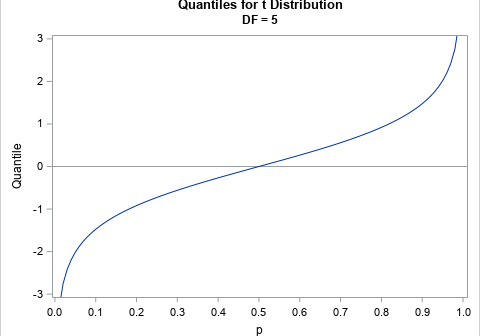
Recently, I needed to solve an optimization problem in which the objective function included a term that involved the quantile function (inverse CDF) of the t distribution, which is shown to the right for DF=5 degrees of freedom. I casually remarked to my colleague that the optimizer would have to
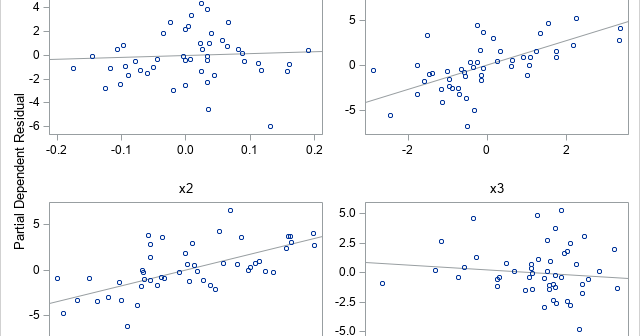
For a linear regression model, a useful but underutilized diagnostic tool is the partial regression leverage plot. Also called the partial regression plot, this plot visualizes the parameter estimates table for the regression. For each effect in the model, you can visualize the following statistics: The estimate for each regression
