The DO Loop
Statistical programming in SAS with an emphasis on SAS/IML programs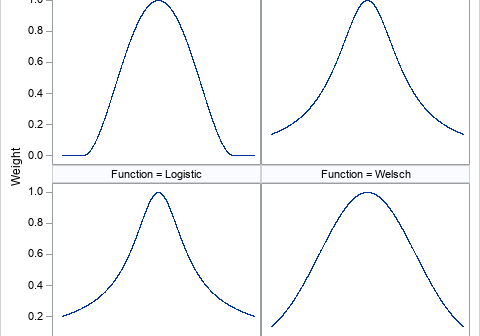
An early method for robust regression was iteratively reweighted least-squares regression (Huber, 1964). This is an iterative procedure in which each observation is assigned a weight. Initially, all weights are 1. The method fits a least-squares model to the weighted data and uses the size of the residuals to determine
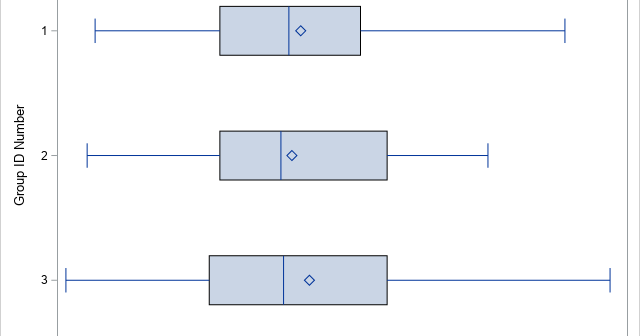
A common question on SAS discussion forums is how to randomly assign observations to groups. An application of this problem is assigning patients to cohorts in a clinical trial. For example, you might have 137 patients that you want to randomly assign to three groups: a control group, a group
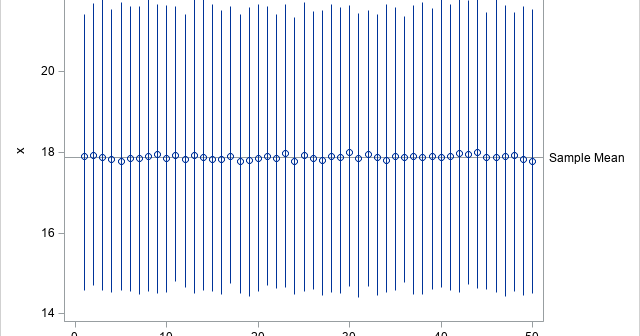
Many modern statistical techniques incorporate randomness: simulation, bootstrapping, random forests, and so forth. To use the technique, you need to specify a seed value, which determines pseudorandom numbers that are used in the algorithm. Consequently, the seed value also determines the results of the algorithm. In theory, if you know
