The DO Loop
Statistical programming in SAS with an emphasis on SAS/IML programs
Real-world data often exhibits extreme skewness. It is not unusual to have data span many orders of magnitude. Classic examples are the distributions of incomes (impoverished and billionaires) and population sizes (small countries and populous nations). The readership of books and blog posts show a similar distribution, which is sometimes
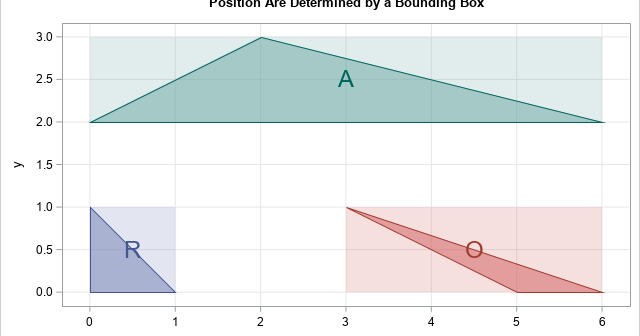
Labeling objects in graphs can be difficult. SAS has a long history of providing support for labeling markers in scatter plots and for labeling regions on a map. This article discusses how the SGPLOT procedure decides where to put a label for a polygon. It discusses the advantages and disadvantages

SAS supports many ways to compute the rank of a numeric variable and to handle tied values. However, sometimes I need to rank the values in a character categorical variable. For example, the values {"Male", "Female", "Male"} have ranks {2, 1, 2} because, in alphabetical order, "Female" is the first-ranked
