The DO Loop
Statistical programming in SAS with an emphasis on SAS/IML programs
Recently, I learned about an elementary programming assignment called the FizzBuzz program. Some companies use this assignment for the first round of interviews with potential programmers. A competent programmer can write FizzBuzz in 5-10 minutes, which leaves plenty of time to discuss other topics. If an applicant can't complete the

In SAS, you can approximate the exponential of a matrix by using the EXPMATRIX function in SAS IML software. This article discusses the exponential of a matrix: what it is, how to compute it, why it is useful, and why you should think of it as a linear map that
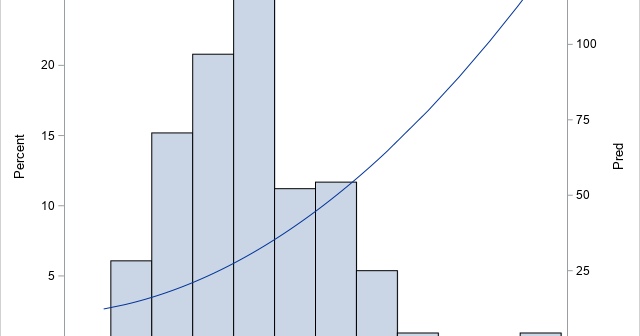
In a previous article, I showed how to overlay a density estimate on a histogram by using the Graph Template Language (GTL). However, a SAS programmer asked how to overlay a curve on a histogram when the curve is not a density estimate. In this case, the vertical axis for
