The DO Loop
Statistical programming in SAS with an emphasis on SAS/IML programs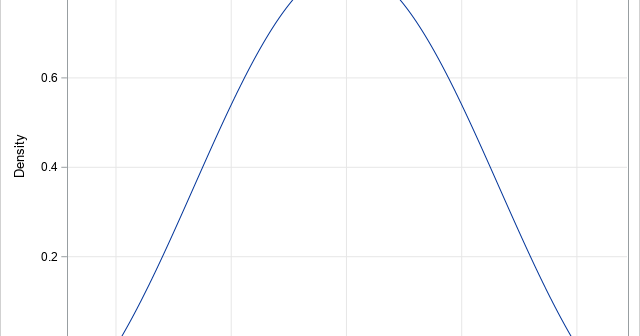
There are dozens of common probability distributions for a continuous univariate random variable. Familiar examples include the normal, exponential, uniform, gamma, and beta distributions. Where did these distributions come from? Well, some mathematician needed a model for a stochastic process and wrote down the equation for the distribution, typically by

Let X be any rectangular matrix. What is the trace of the crossproducts matrix, X'*X? Interestingly, you do not need to form the crossproducts matrix to compute the answer! It turns out that tr(X'*X) equals the sum of the squared elements of X. Theorem: For any matrix, X, the trace
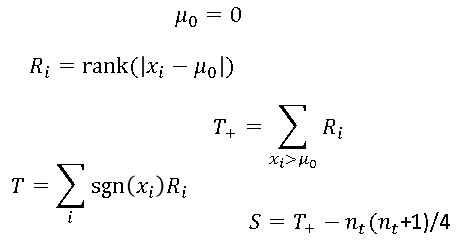
In a previous article, I discussed the Wilcoxon signed rank test, which is a nonparametric test for the location of the median. The Wikipedia article about the signed rank test mentions a variation of the test due to Pratt (1959). Whereas the standard Wilcoxon test excludes values that equal μ0
