The DO Loop
Statistical programming in SAS with an emphasis on SAS/IML programs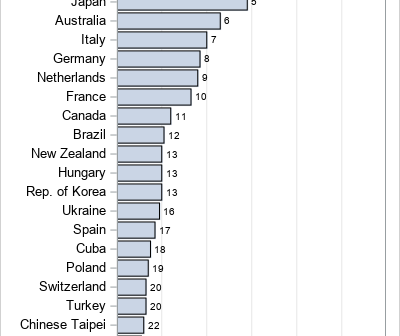
A previous article discusses the geometry of weighted averages and shows how choosing different weights can lead to different rankings of the subjects. As an example, I showed how college programs might rank applicants by using a weighted average of factors such as test scores. "The best" applicant is determined
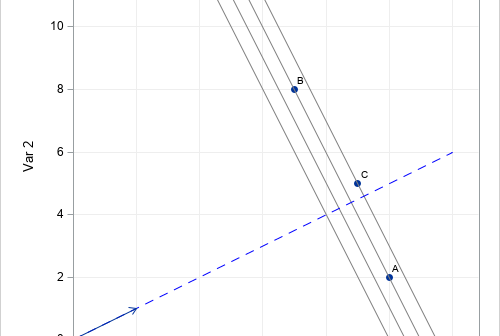
People love rankings. You've probably seen articles about the best places to live, the best colleges to attend, the best pizza to order, and so on. Each of these is an example of a ranking that is based on multiple characteristics. For example, a list of the best places to
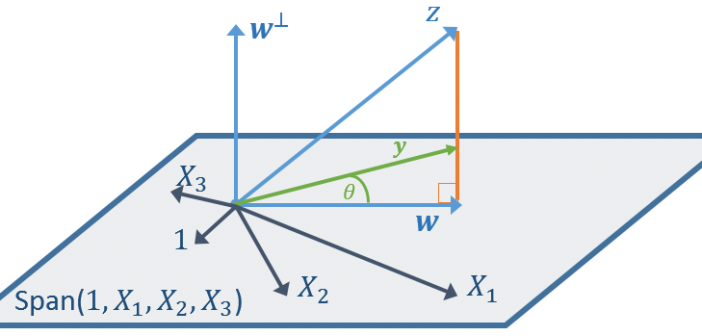
One of the benefits of using the SWEEP operator is that it enables you to "sweep in" columns (add effects to a model) in any order. This article shows that if you use the SWEEP operator, you can compute a SSCP matrix and use it repeatedly to estimate any linear
