Graphically Speaking
Data Visualization with a focus on SAS ODS Graphics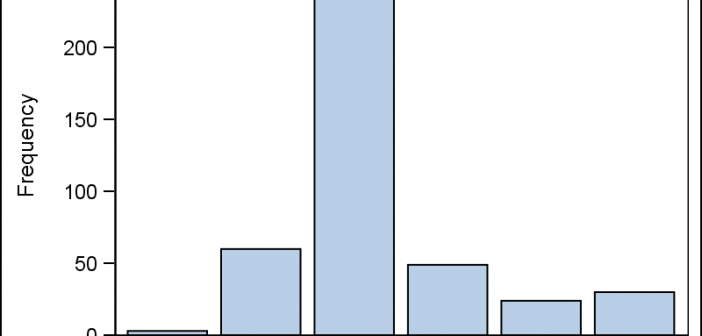
This is the 2nd installment of the "Getting Started" series, and the audience is the user who is new to the SG Procedures. It is quite possible that an experienced users may also find some useful nuggets here. One of the most popular and useful graph types is the Bar
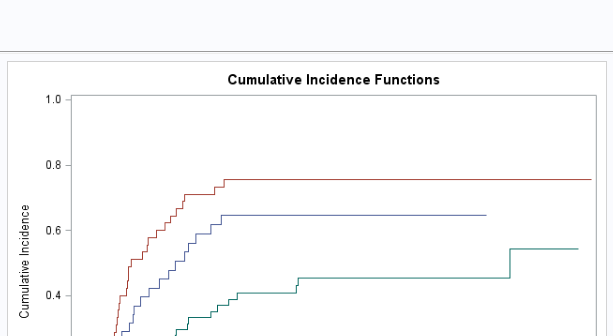
In my previous post, I showed you how to change the titles in graphs produced by analytical procedures; today I will show you how to remove subtitles that procedures display on some output pages. The following step creates output that contains a SAS title ('Illustrate the CIF Plot'), a PROCTITLE
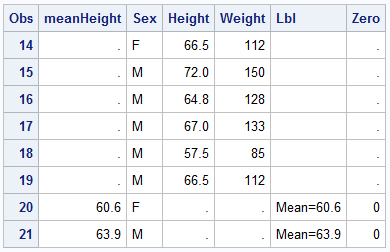
Last week a user asked about BY variable group processing for SGAnnotate with SGPLOT procedure. The user provided a simple use case for the question (always a good idea) using the sashelp.class data set. The graph included a display of reference lines for the mean value of height using annotation. The

