The DO Loop
Statistical programming in SAS with an emphasis on SAS/IML programs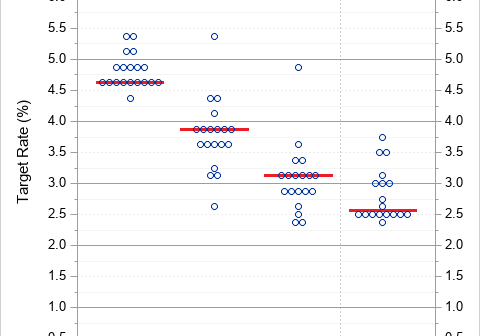
A dot plot is a standard statistical graphic that displays a statistic (often a mean) and the uncertainty of the statistic for one or more groups. Statisticians and data scientists use it in the analysis of group data. In late 2023, I started noticing headlines about "dot plots" in the
Recently, I saw a scatter plot that displayed the ticks, values, and labels for a vertical axis on the right side of a graph. In the SGPLOT procedure in SAS, you can use the Y2AXIS option to move an axis on the right side of a graph. Similarly, you can

A recent article describes how to estimate coefficients in a simple linear regression model by using maximum likelihood estimation (MLE). One of the nice properties of an MLE formulation is that you can compare a large model with a nested submodel in a natural way. For example, if you can
