The DO Loop
Statistical programming in SAS with an emphasis on SAS/IML programs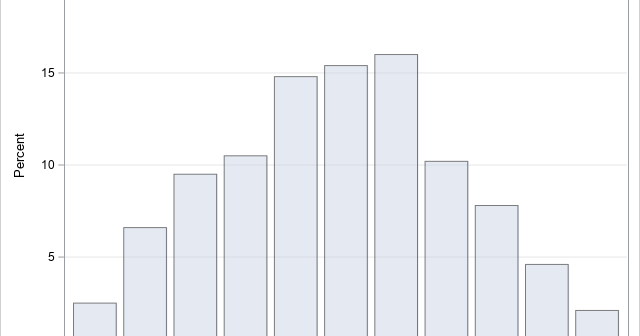
At a recent conference in Las Vegas, a presenter simulated the sum of two dice and used it to simulate the game of craps. I write a lot of simulations, so I'd like to discuss two related topics: How to simulate the sum of two dice in SAS. This is
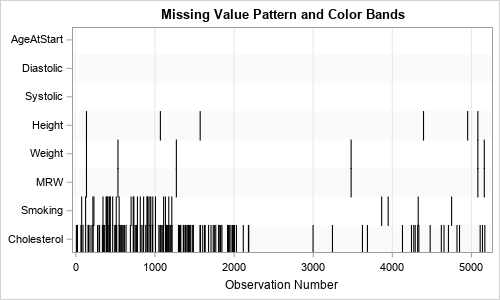
Years ago, I wrote an article that showed how to visualize patterns of missing data. During a recent data visualization talk, I discussed the program, which used a small number of SAS IML statements. An audience member asked whether it is possible to construct the same visualization by using only
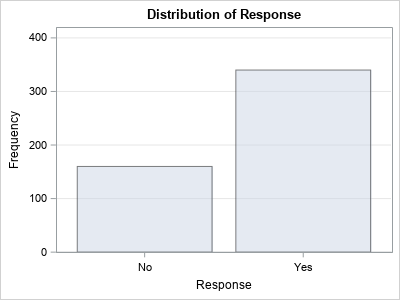
A SAS programmer wanted to estimate a proportion and a confidence interval (CI), but didn't know which SAS procedure to call. He knows a formula for the CI from an elementary statistics textbook. If x is the observed count of events in a random sample of size n, then the
