The DO Loop
Statistical programming in SAS with an emphasis on SAS/IML programs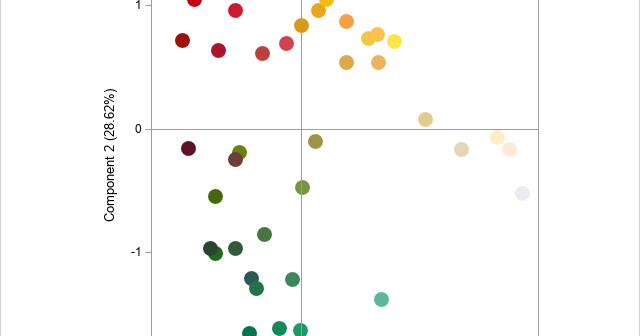
In a previous article, I visualized seven Christmas-themed palettes of colors, as shown to the right. You can see that the palettes include many red, green, and golden colors. Clearly, the colors in the Christmas palettes are not a random sample from the space of RGB colors. Rather, they represent
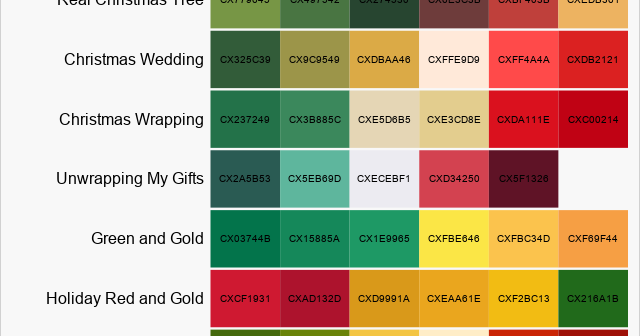
In data visualization, colors can represent the values of a variable in a choropleth map, a heatmap, or a scatter plot. But how do you visualize a palette of colors from the RGB or hexadecimal values of the colors? One way is to use the HEATMAPDISC subroutine in SAS/IML, which
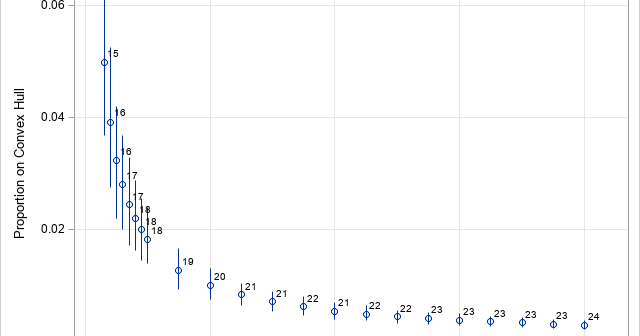
While discussing how to compute convex hulls in SAS with a colleague, we wondered how the size of the convex hull compares to the size of the sample. For most distributions of points, I claimed that the size of the convex hull is much less than the size of the
