The DO Loop
Statistical programming in SAS with an emphasis on SAS/IML programs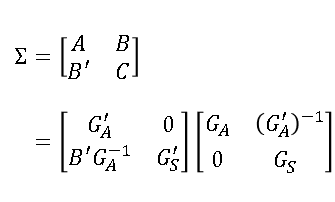
You can use the Cholesky decomposition of a covariance matrix to simulate data from a correlated multivariate normal distribution. This method is encapsulated in the RANDNORMAL function in SAS/IML software, but you can also perform the computations manually by calling the ROOT function to get the Cholesky root and then
Last year, I wrote almost 100 posts for The DO Loop blog. My most popular articles were about data visualization, statistics and data analysis, and simulation and bootstrapping. If you missed any of these gems when they were first published, here are some of the most popular articles from 2021:
Suppose you are creating a craft project for the Christmas holidays, and you want to choose a palette of Christmas colors to give it a cheery holiday appearance. You could use one of the many online collections of color palettes to choose a Christmas-themed palette. However, I didn't want to
