The DO Loop
Statistical programming in SAS with an emphasis on SAS/IML programs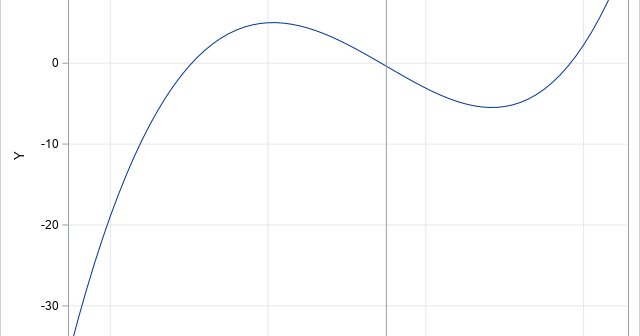
A SAS programmer asked if it is possible to numerically find an inflection point for a univariate function, f(x). Yes! This can be solved as a variation of a classic numerical root-finding problem. Recall that an inflection point is a value (call it x0) in the domain where the graph
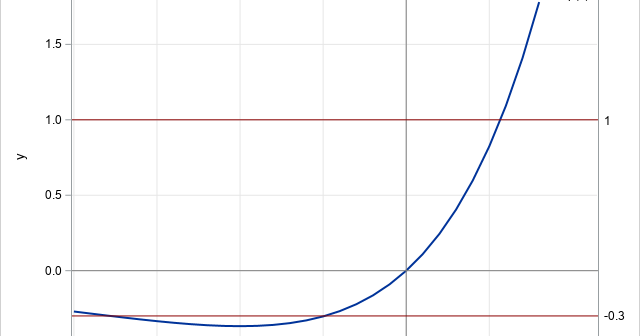
I previously wrote an article about the Lambert W function. The Lambert W function is the inverse of the function g(x) = x exp(x). This means that you can use it to find the value of x such that g(x)=c for any value of c in the range of g, which
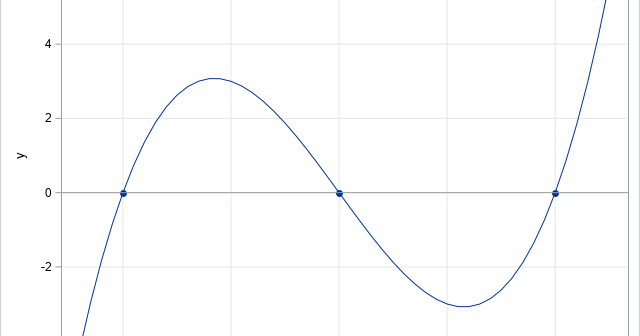
A SAS programmer had many polynomials for which he wanted to compute the real roots. By the Fundamental Theorem of Algebra, every polynomial of degree d has d complex roots. You can find these complex roots by using the POLYROOT function in SAS IML. The programmer only wanted to output
