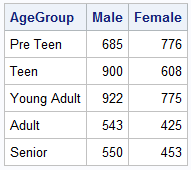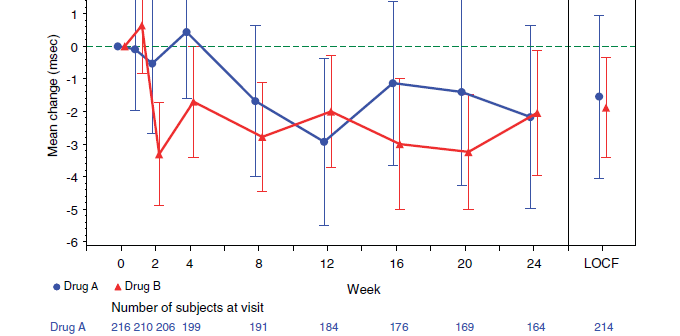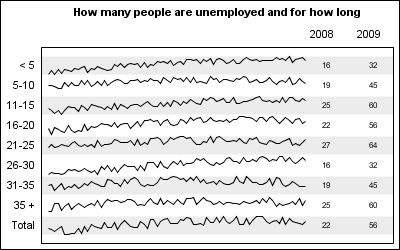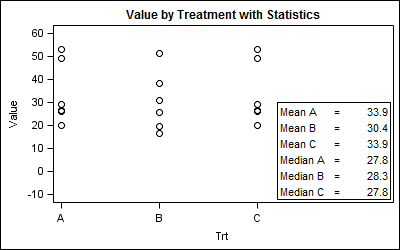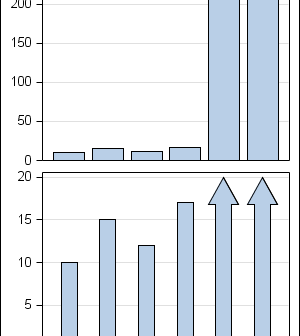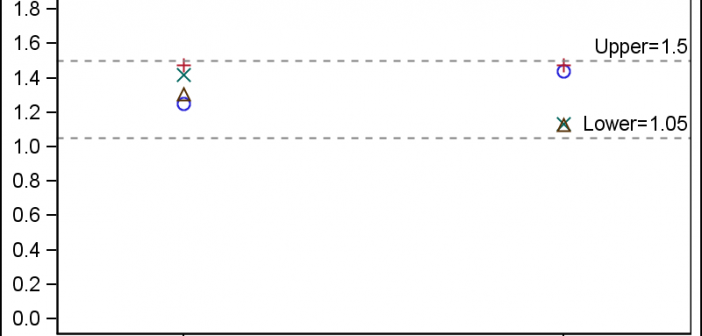
In the Clinical Research domain, there is often the need to display lab values by treatment or test and it is often useful to view this data along with reference lines showing the normal ranges. The obvious way is to use reference lines to denote the normal ranges. SGPLOT Code: proc sgplot data=band; scatter x=x y=y