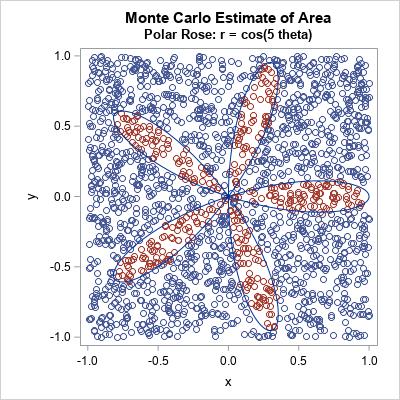
Queuing up to wait for services is a nearly universal experience. We routinely arrange ourselves in single file lines at the bank, at retail stores, and at the fast-food drive-through. Since the COVID pandemic hit, we've increasingly waited in lines to ensure our health – lining up to be seen