
Starting your data scientist journey? Want to build your own predictive models? SAS' Xavier Bizoux shows you how to use SAS Visual Analytics to identify which model likely to perform the best.

Starting your data scientist journey? Want to build your own predictive models? SAS' Xavier Bizoux shows you how to use SAS Visual Analytics to identify which model likely to perform the best.

This blog is a part of a series on the Data Science Pilot Action Set. In this blog, we discuss updates to Visual Data Mining and Machine Learning with the release of Viya 3.5. In the middle of my blog series, SAS released Viya 3.5. Included in Viya 3.5 was the

The new method tackles the challenge of missing features under the multi-task learning framework. The proposed method is effective for prediction and model estimation when missing data is present.
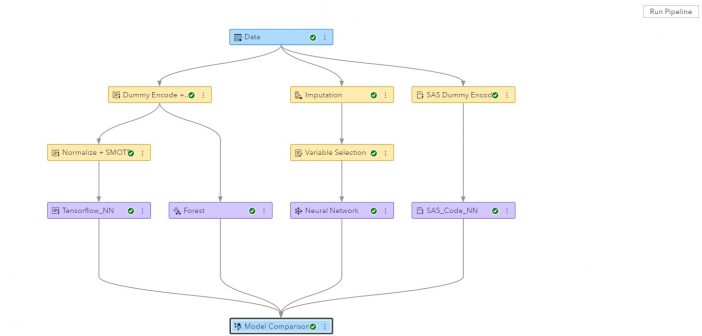
SAS Model Studio lets modelers use SAS alongside open source to create and compare models in a pipeline and project. Debugging, model comparison, and visual pipelines are included.
Computer vision can augment radiologists and make the image interpretation process cheaper, faster and more accurate. The ultimate goal is to achieve a better patient outcome facilitated by the use of computer vision.
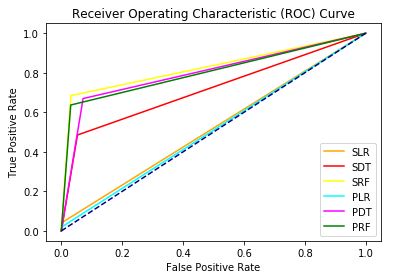
This blog focuses on using SASPy for modeling and machine learning.

Data scientists naturally use a lot of machine learning algorithms, which work well for detecting patterns, automating simple tasks, generalizing responses and other data heavy tasks. As a subfield of computer science, machine learning evolved from the study of pattern recognition and computational learning theory in artificial intelligence. Over time, machine learning has borrowed from many

SAS Viya is a cloud-enabled, in-memory analytics engine which allows for rapid analytics insights. Viya utilizes the SAS Cloud Analytics Services (CAS) to perform various actions and tasks. Best of all, CAS is accessible from various interfaces including R. In this blog, I will go through a few blocks one of my notebooks, which moves through an analytics workflow using R and SAS.

The dsAutoMl action is all that and a bag of chips! In this blog, we took over all aspects of the data science workflow using just one action.
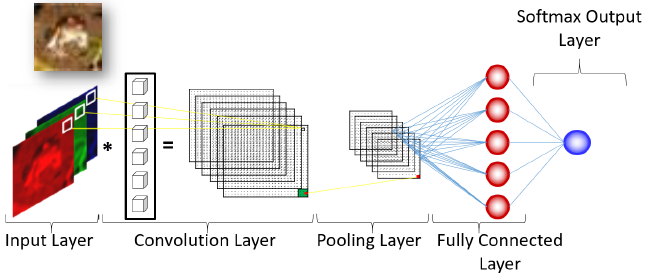
Jordan Bakerman's session at ODSC Europe inspired this post, which provides an overview of deep learning and how factorization machines work.