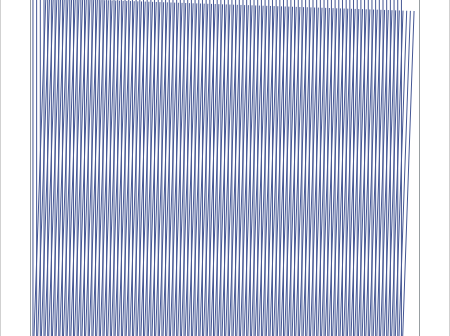
Since the COVID-19 pandemic began, video presentations and webcasts have become a regular routine for many of us. On days that I will be using my webcam, I wear a solid-color shirt. If I don't plan to be on camera, I can wear a pinstripe Oxford shirt. Why the difference?