The DO Loop
Statistical programming in SAS with an emphasis on SAS/IML programs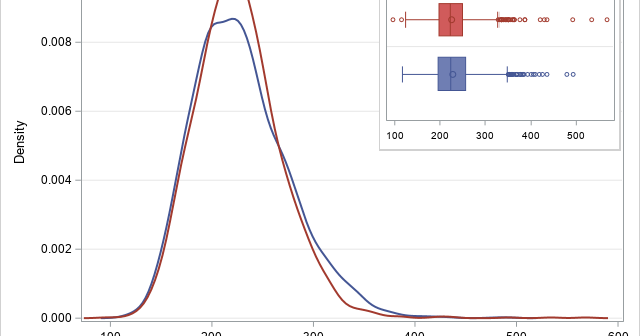
Did you know that you can embed one graph inside another by using PROC SGPLOT in SAS? A typical example is shown to the right. The large graph shows kernel density estimates for the distribution of the Cholesterol variable among male and female patients in a heart study. The small

I don't often use the SG annotation facility in SAS for adding annotations to statistical graphics, but when I do, I enjoy the convenience of the SG annotation macros. I can never remember the details of the SG annotation commands, but I know that the SG annotation macros will create
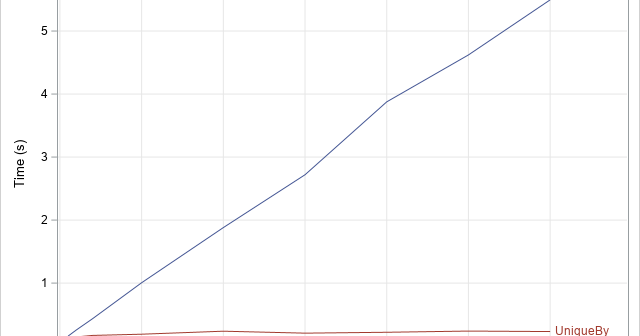
Many SAS procedures support a BY statement that enables you to perform an analysis for each unique value of a BY-group variable. The SAS IML language does not support a BY statement, but you can program a loop that iterates over all BY groups. You can emulate BY-group processing by
