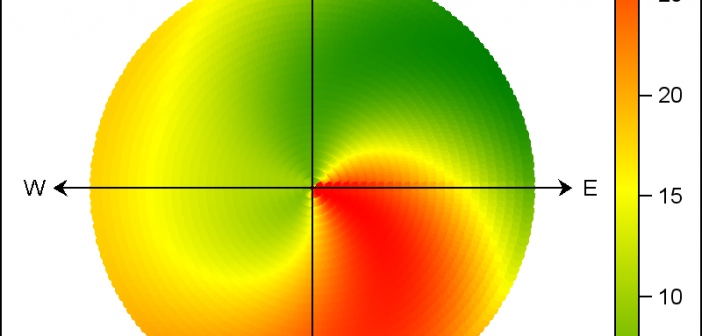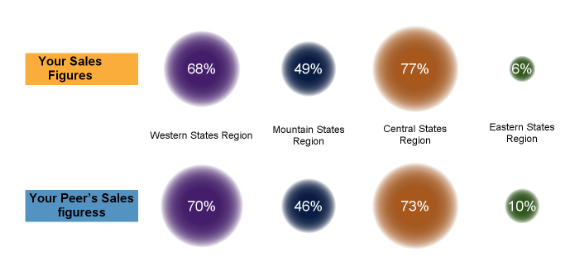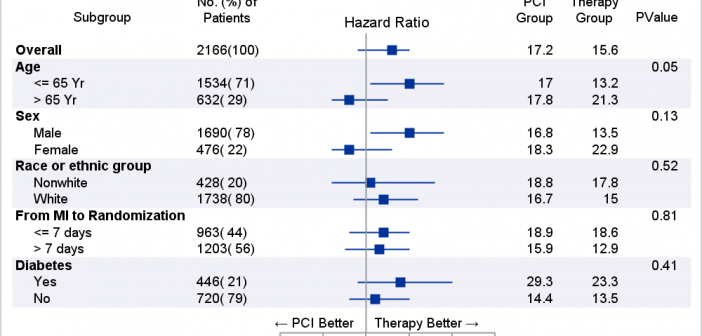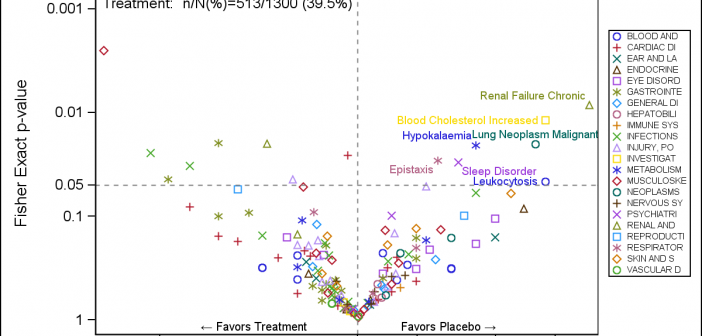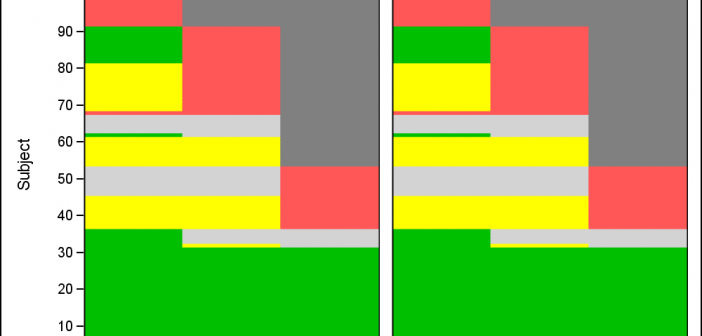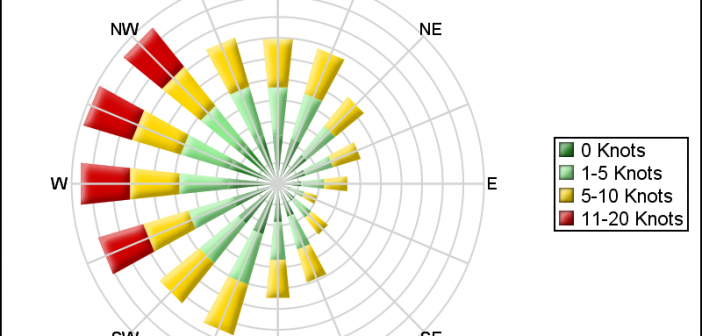
Last week I posted an article on displaying polar graph using SAS. When the measured data (R, Theta) are in the polar coordinates as radius and angle, then this data can be easily transformed into the XY space using the simple transform shown below. x=r*cos(theta * PI / 180); y=r*sin(theta * PI