A typical day brings countless business decisions that affect everything from profitability to customer experience. What is a reasonable price point? Which audience segments should I personalize offers for? When should I recommend specific content earlier in a customer journey?
Daily decisions like these can alter the trajectory of a brand’s business. And while one bad move may not seem detrimental, hundreds or thousands of such operational decisions can be. So, it’s important that each decision is made with the best, most accurate information – while remaining consistent with organizational policy.
In a previous post, I addressed the topic of predictive next best actions. In summary, it discussed how this strategy aspires to:
- Align with key business imperatives.
- Deliver through customer-interaction channels.
- Inform targeted offers.
- Shape multichannel conversations.
The post showed how a user of SAS Customer Intelligence 360 can construct analytical models. The featured use case focused on propensity-based customer targeting by offer type.
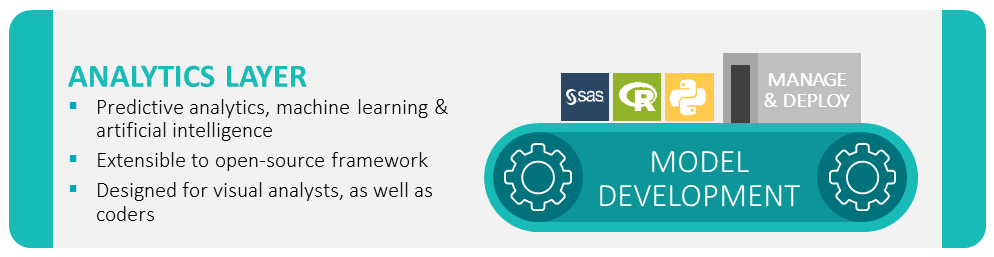
The use case ended on how to leverage analytical scoring. The output leads to a decision concerning the best offer to deliver within a touchpoint. The decision can made in real time for inbound interactions and triggered for outbound communications. The decision will select only one (the best) proposition out of the possible offers, depending on the individual’s propensity to buy.
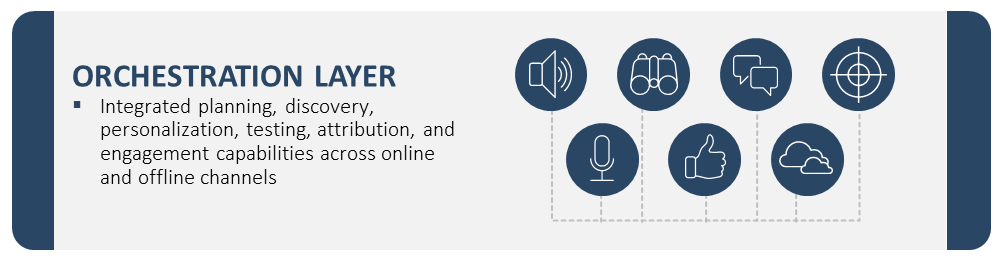
Is there more to next best action strategies than propensity scores and multichannel orchestration?
Absolutely. It's important to objectively realize that your brand or product isn't the center of your consumer's world. In fact, most marketing-centric content is perceived as an interruption to a customer-oriented experience. The key to micro-moment marketing is to embrace the notion that a few seconds exist to capture the attention of your target. Within that tiny window, brands are challenged to convey a communication that resonates.
Ultimately, the customer journey is just an amalgamation of micro-moments across channels, devices and varying flavors of intent. This leads us to the importance of decision management, and specifically:
- Real-time event processing with contextual data.
- Contact policies and offer eligibility.
- Accelerated model deployment.
- Model management.
- Integration with analytic and orchestration technology layers.
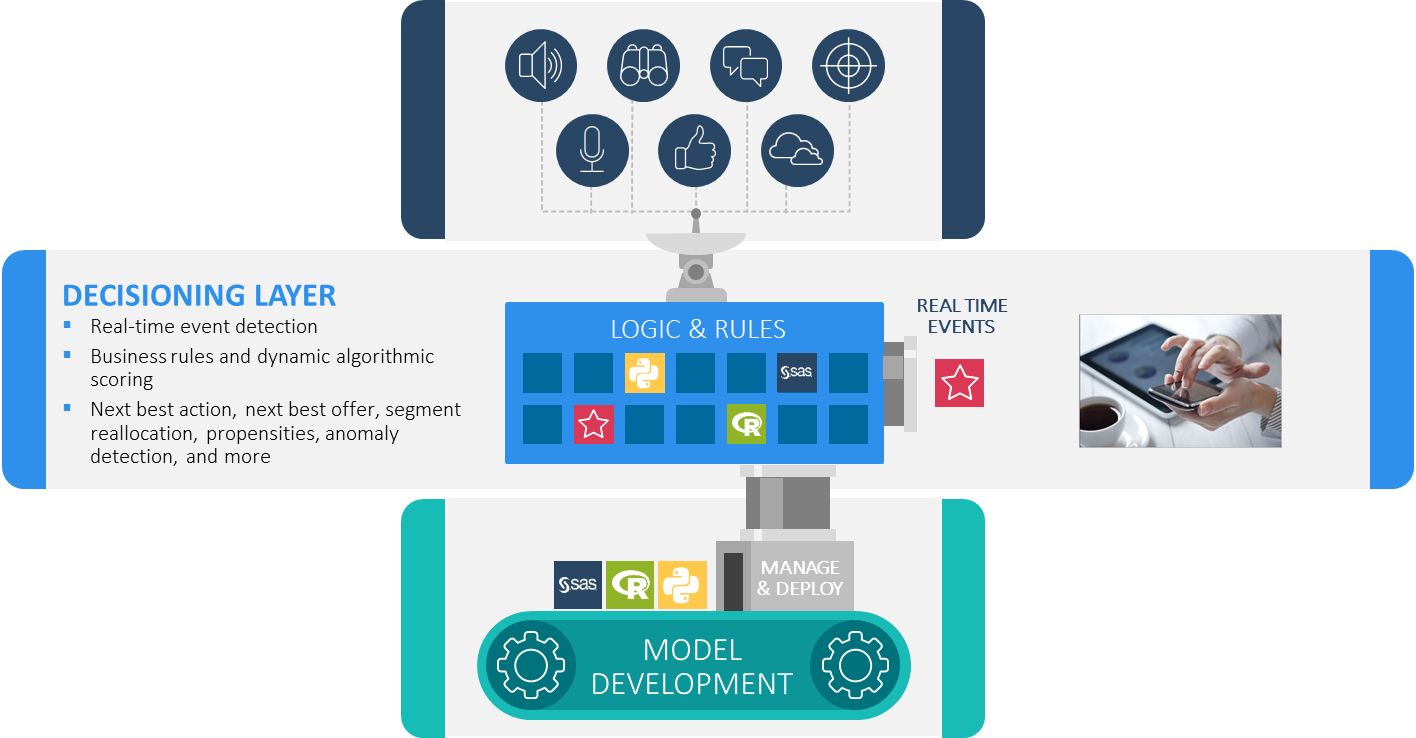
(Figure 3: SAS Customer Intelligence 360 - Decisioning layer)
Let’s go through a basic example. You have a prospect with a high propensity for a specific offer, that engages through social channels, but is under the age of 18. Your organization’s policy is not to advertise to individuals below a specific age threshold, regardless of how high her propensity score is. The decisioning layer allows you to combine analytical models, business rule sets and conditional logic into customer treatments and publish the decisions for orchestration within SAS Customer Intelligence 360.
Rule sets capture the logic of business decisions by allowing users to codify the decision-making process used by your organization. The rules make the decision-making process transparent and adaptable, enabling brands to respond quickly to new information about customers, segments and markets.
Allow me to reveal a peek into the design principles for SAS Customer Intelligence 360, where the technology is intended to resemble the anatomy of the human brain. There are two distinct hemispheres.
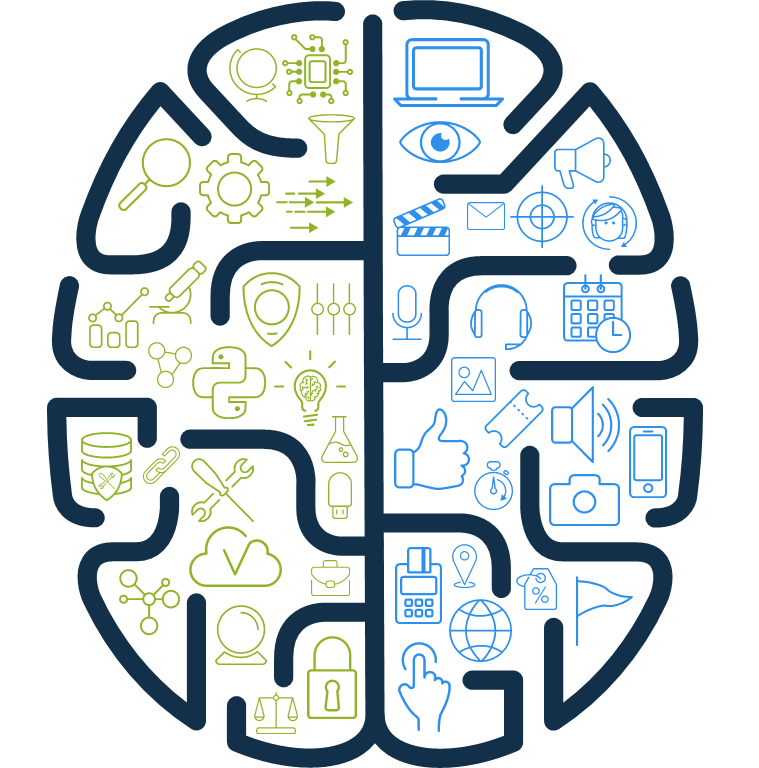
The left hemisphere is associated with analytical, logical and fact-oriented thinking. The right side is associated with creative, intuitive, and visual thinking. This translates to:
- The strength of the left side links tightly with authoring and deploying predictive/machine learning models, mapping to the analytic and decisioning layers referenced above.
- The right side facilitates the orchestration layer of marketing activity across planning, creative and operations.
Together the intent is to better understand and manage customer activity, regardless of channel, in alignment with a brand’s goals and objectives. At the end of the day, the analytical minded, and the creative minded, need to be in lock step with one another. This is how the whole-brain approach of SAS Customer Intelligence 360 and SAS Decision Manager is facilitated.
How would this work on a website or mobile app?
Assume I have been interacting with a brand’s digital properties across a visitor journey. After being targeted within a mobile app session to obtain an e-book, I am redirected to the website to acquire the content.
When I click on the download e-book button on this page, this will generate an event in SAS Customer Intelligence 360. The question is how do I configure event monitoring? Within the software’s user interface, there are a variety of digital interaction types that can be captured.

For this example, we select the click event type. After doing so, we can navigate to the web page with the download e-book call-to-action, and visually select the element (as opposed to codifying its location). A single click generates the corresponding HTML DIV code, and the contextual monitoring begins for every user that clicks that specific button.
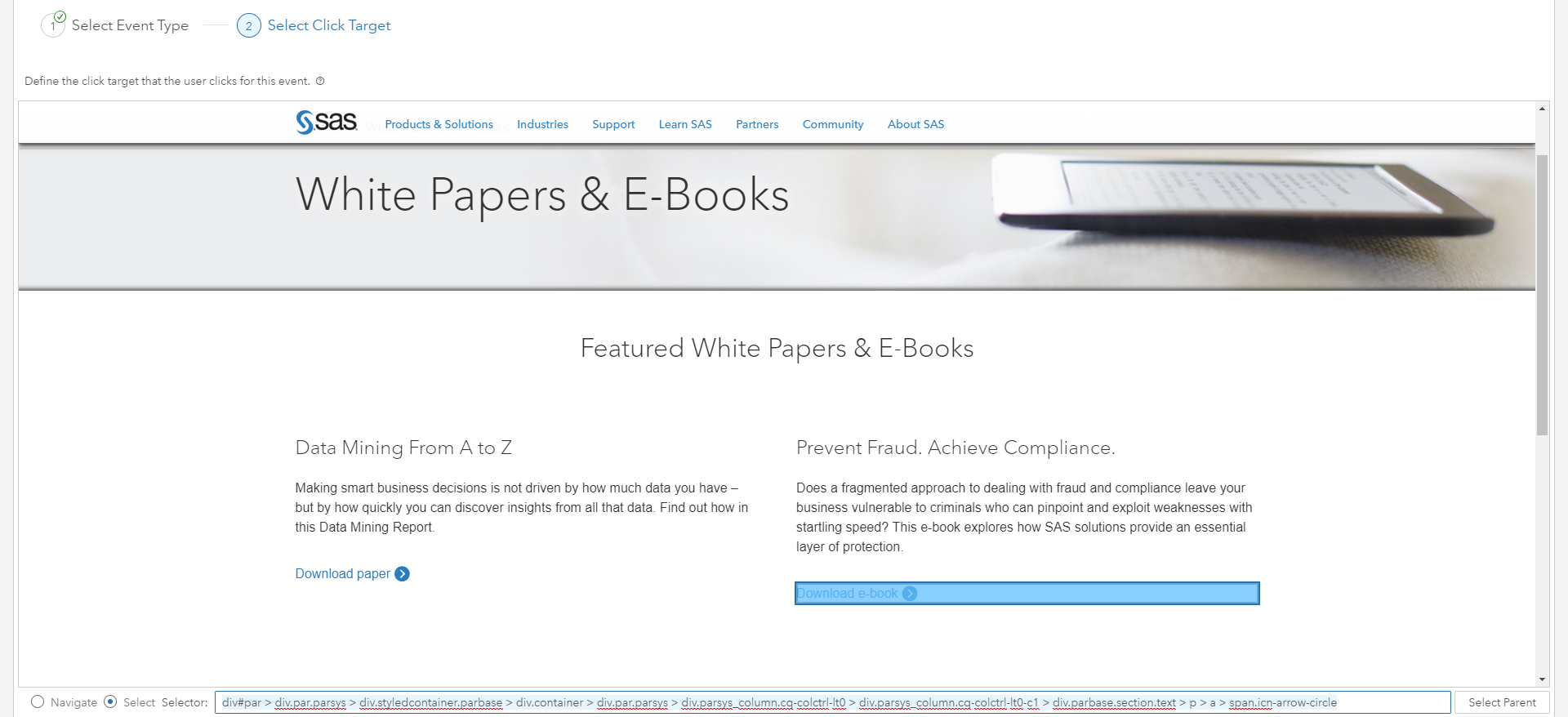
Now that we can observe every instance when that interaction occurs, we want SAS Customer Intelligence 360 to contact SAS Decision Manager in real time for every visitor journey that meets the event definition. To do so, an agent is established to make the API connection.
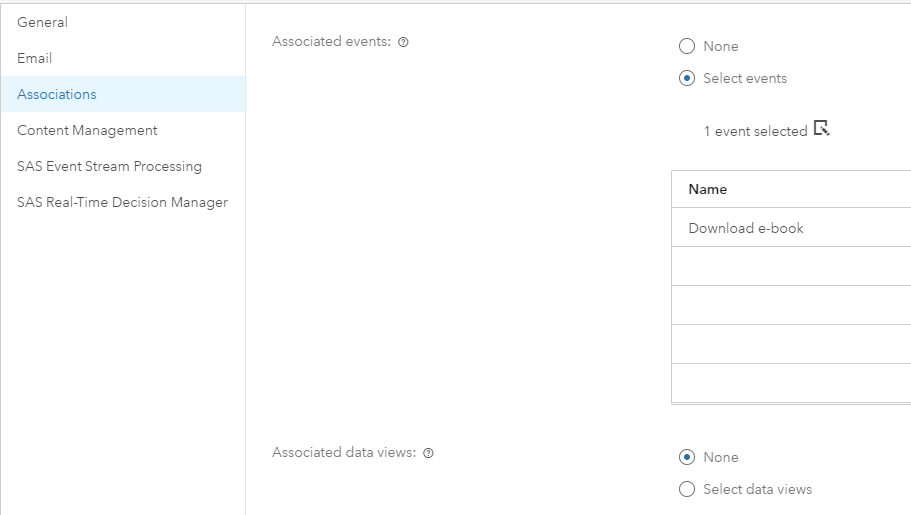
Once the credentials are set, the association of the visitor interactions with the download e-book button and SAS Decision Manager can be defined.
The value of unifying these two technologies within the SAS platform creates powerful benefits:
- SAS Customer Intelligence 360 can be used to stream real-time behavioral events to SAS Decision Manager.
- Real-time events from digital touchpoints can trigger decisions in SAS Decision Manager. These decisions can be used with other data sources such as CRM, demographics, transaction history, third-party data, etc.
- Decisions executed by SAS Decision Manager can manage and execute analytic models, business rules and conditional logic to return a recommended course of action.
Let’s walk through this, one step at a time. When the e-book download web event occurs, SAS Decision Manager will use the SAS Micro Analytic Service to:
- Query the latest CRM values for this specific customer regarding their education, income, age and occupation.
- Immediately apply a business rule that offer personalization cannot be targeted at individuals aged under 18.
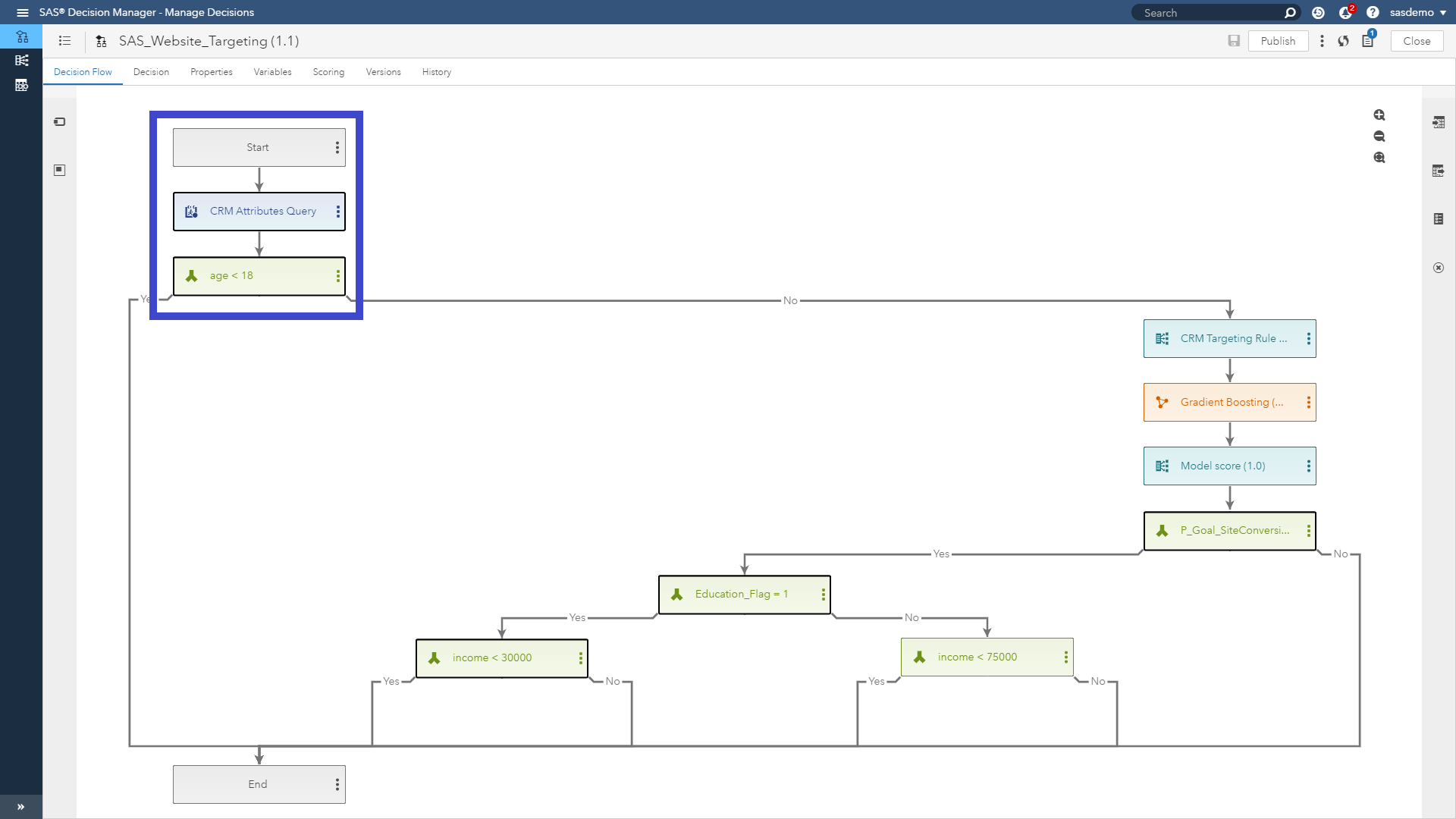
- Run an auto-tuned, gradient boosting model to produce a fresh propensity score using both online data and offline input data sources.
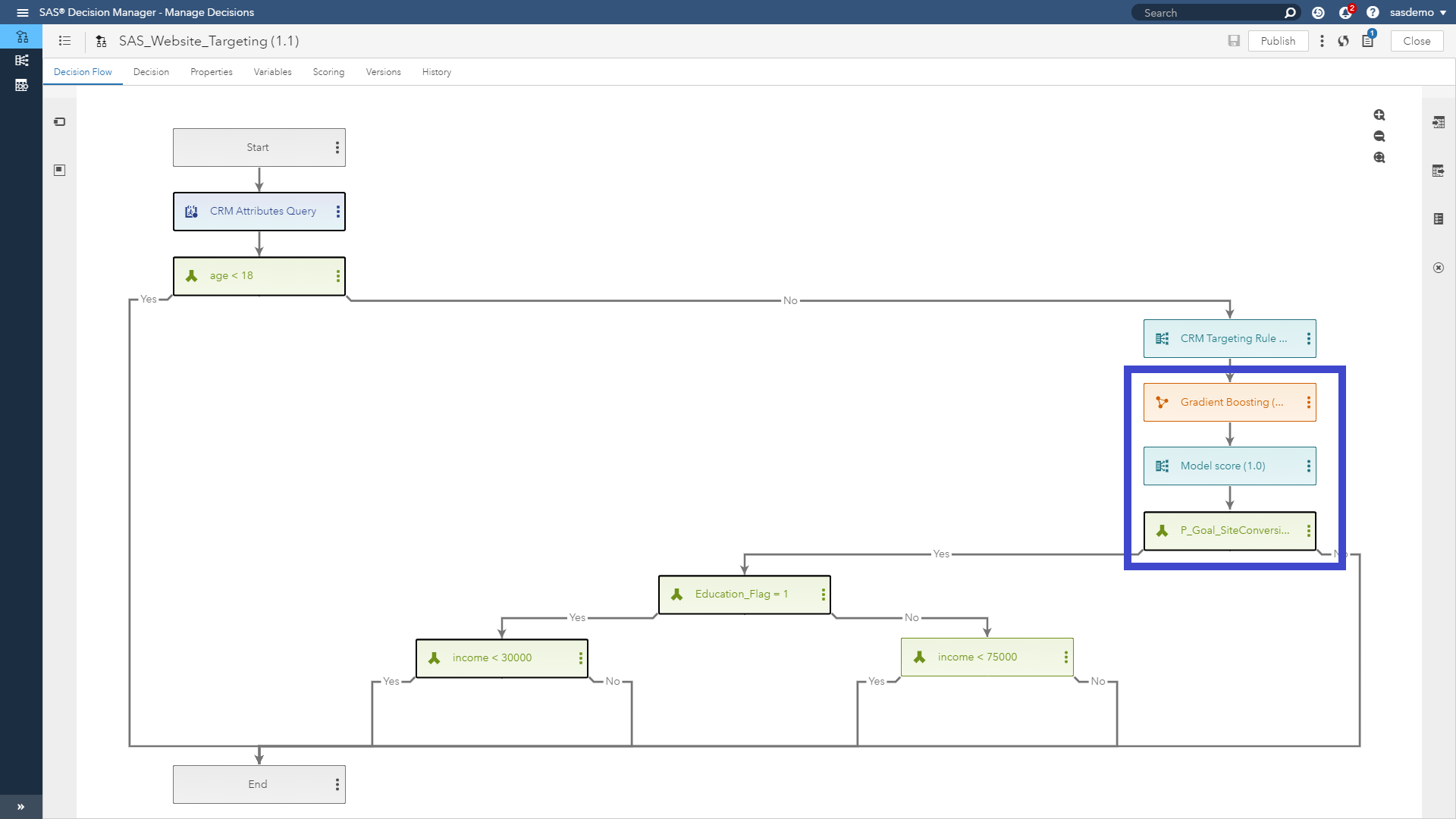
SAS Decision Manager is part of the SAS Viya platform. Any modeling project authored, from singular algorithmic approaches to tournaments of machine-learning applications, can be exploited.
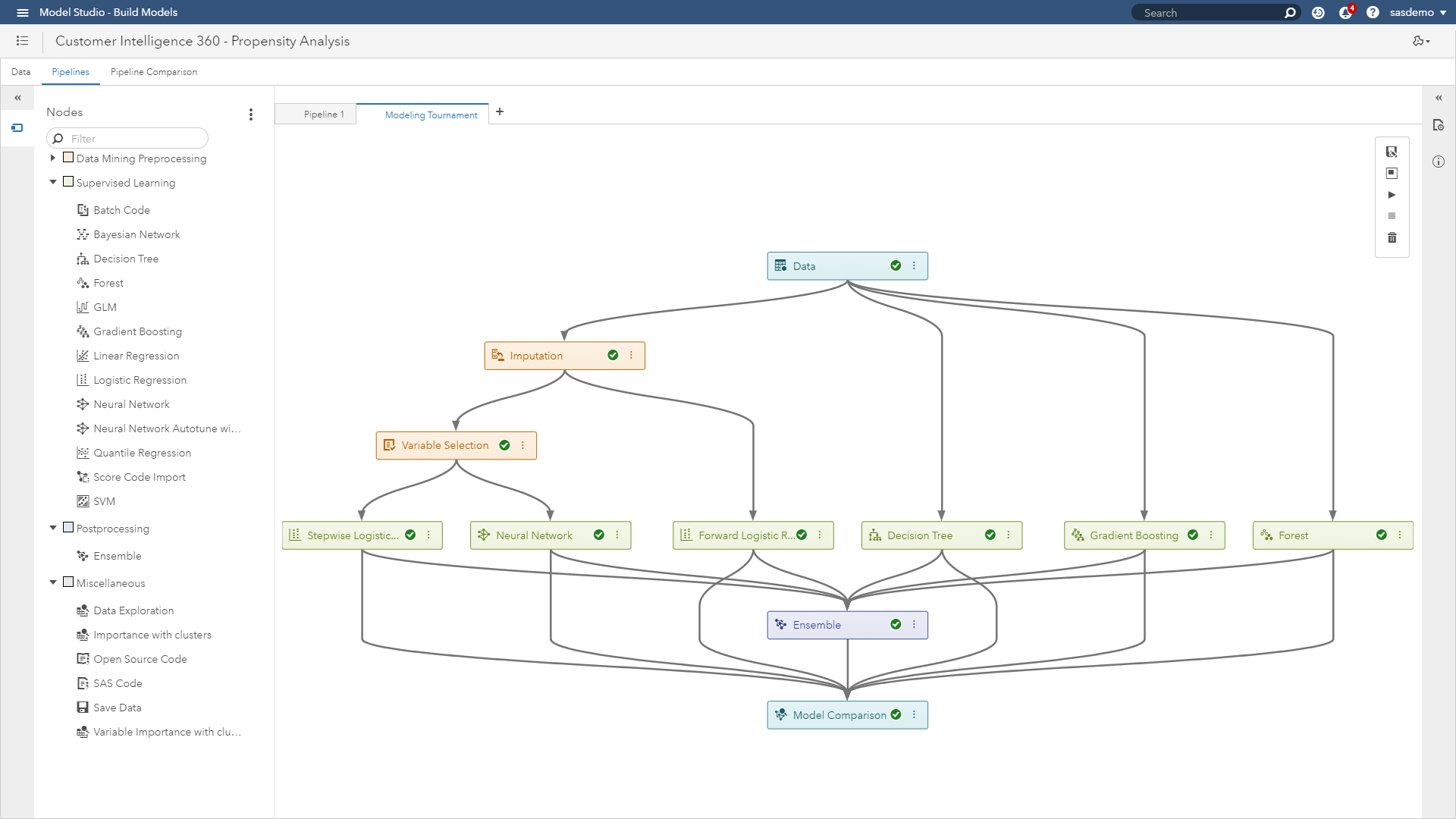
- Apply conditional logic using different combinations of CRM business rules and analytical propensity scores.
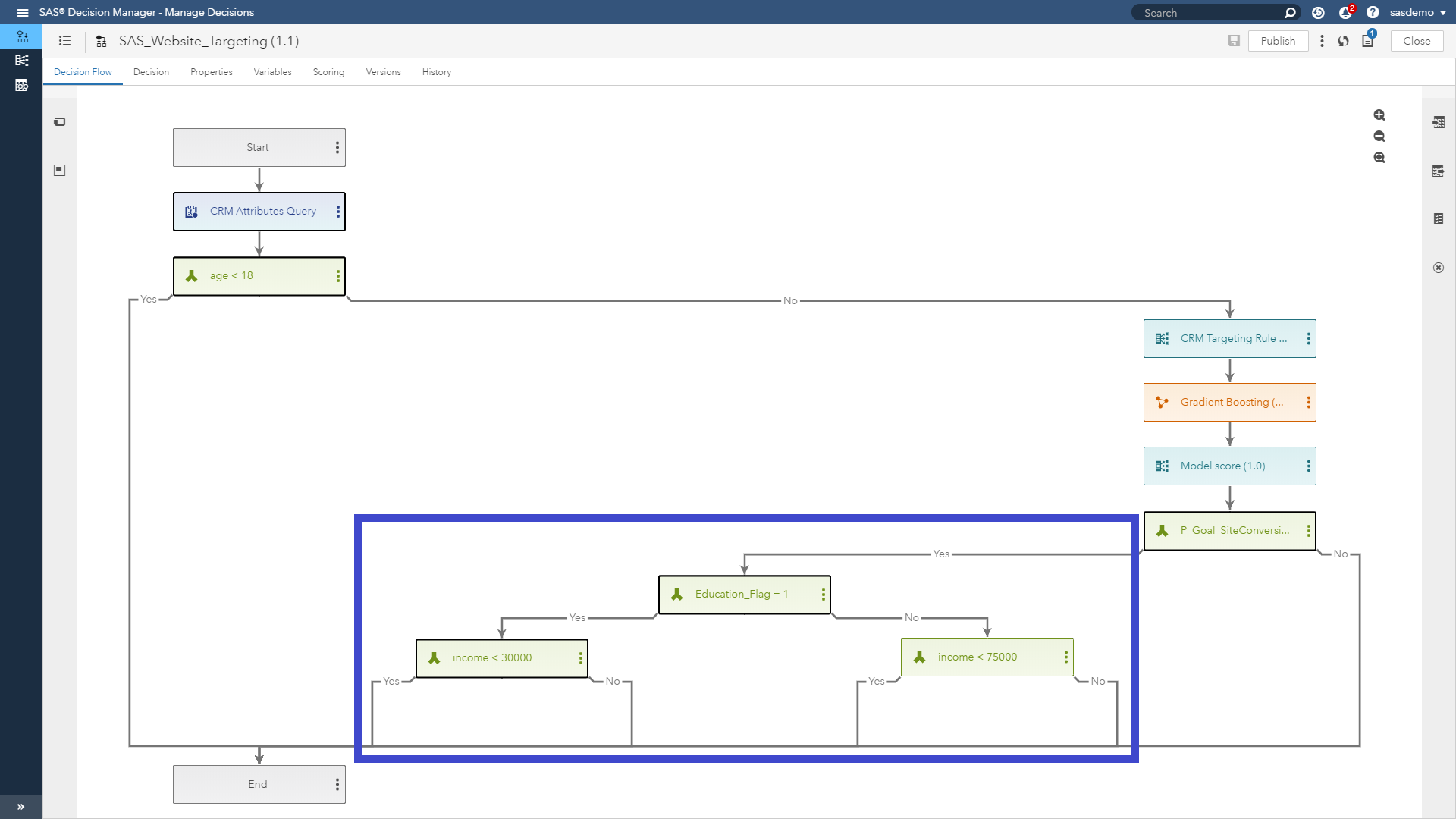
- Based on the customer’s assignment, produce four actionable segments, and inform SAS Customer Intelligence 360 how to personalize the offer on the next page of the current web visit.
The SAS Micro Analytic Service is part of SAS Decision Manager. It is powerful feature designed to execute analytical models and business rules against the latest data from online channels, combined with data from operational databases and other data sources. This entire process executes in milliseconds and works with SAS Customer Intelligence 360 to increase personalization precision without disrupting the customer’s digital experience.
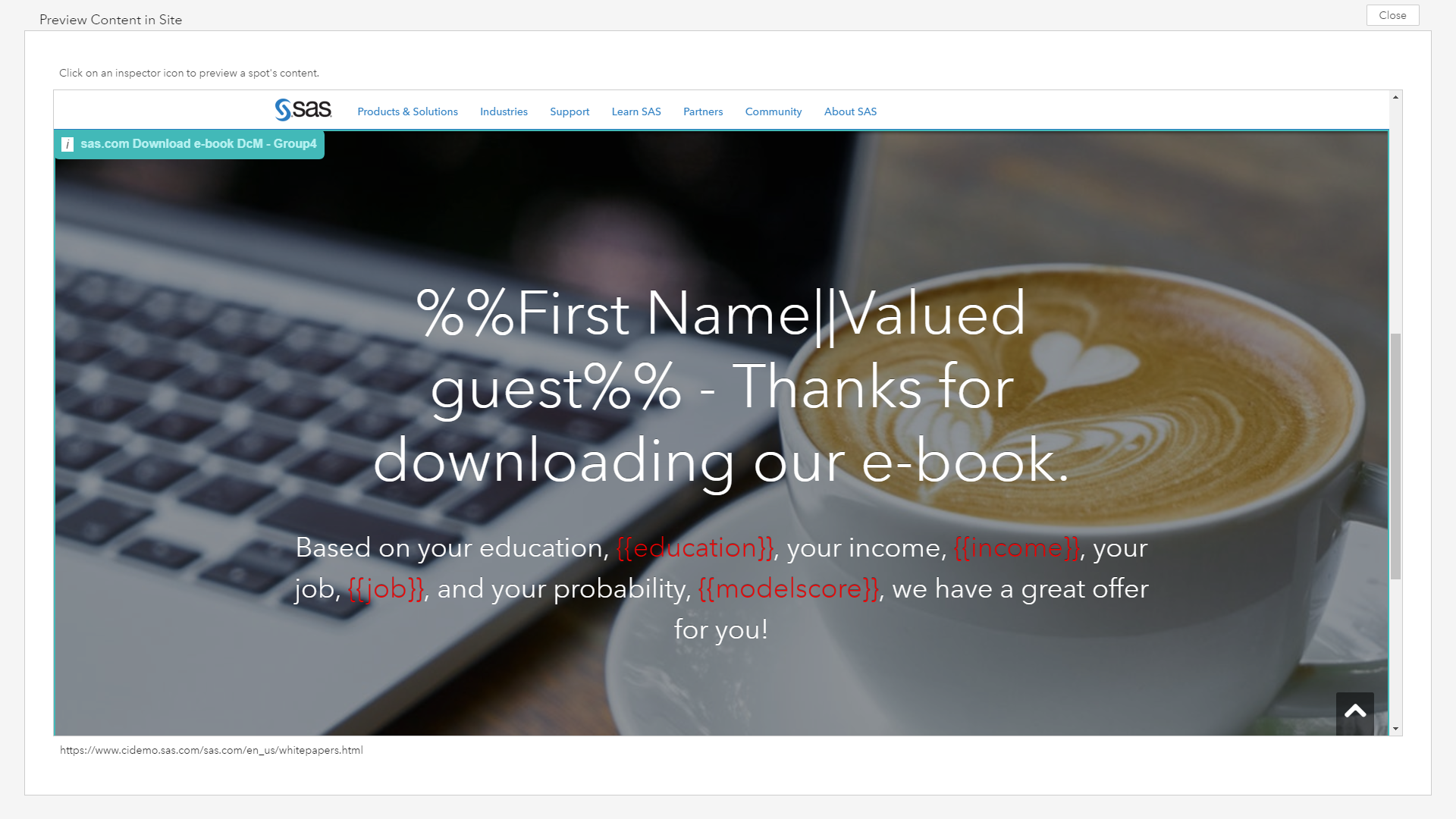
In Figure 14, users can preview what will be displayed for the web visitor based on their segment assignment. In this example, I have used merge tags to transparently show how the CRM and model score values derived from SAS Decision Manager can be recognized by SAS Customer Intelligence 360 to support the personalization use case.
An HTML creative that is associated with a next-best-action offer can include dynamic properties, which are associated with attributes from an external system. The properties can be used as dynamic merge tag variables in the HTML creative. When SAS Decision Manager sends a request to SAS Customer Intelligence 360 to deliver the creative with attribute values, those values are used as merge tag values when the creative is delivered to the desired web page spot.
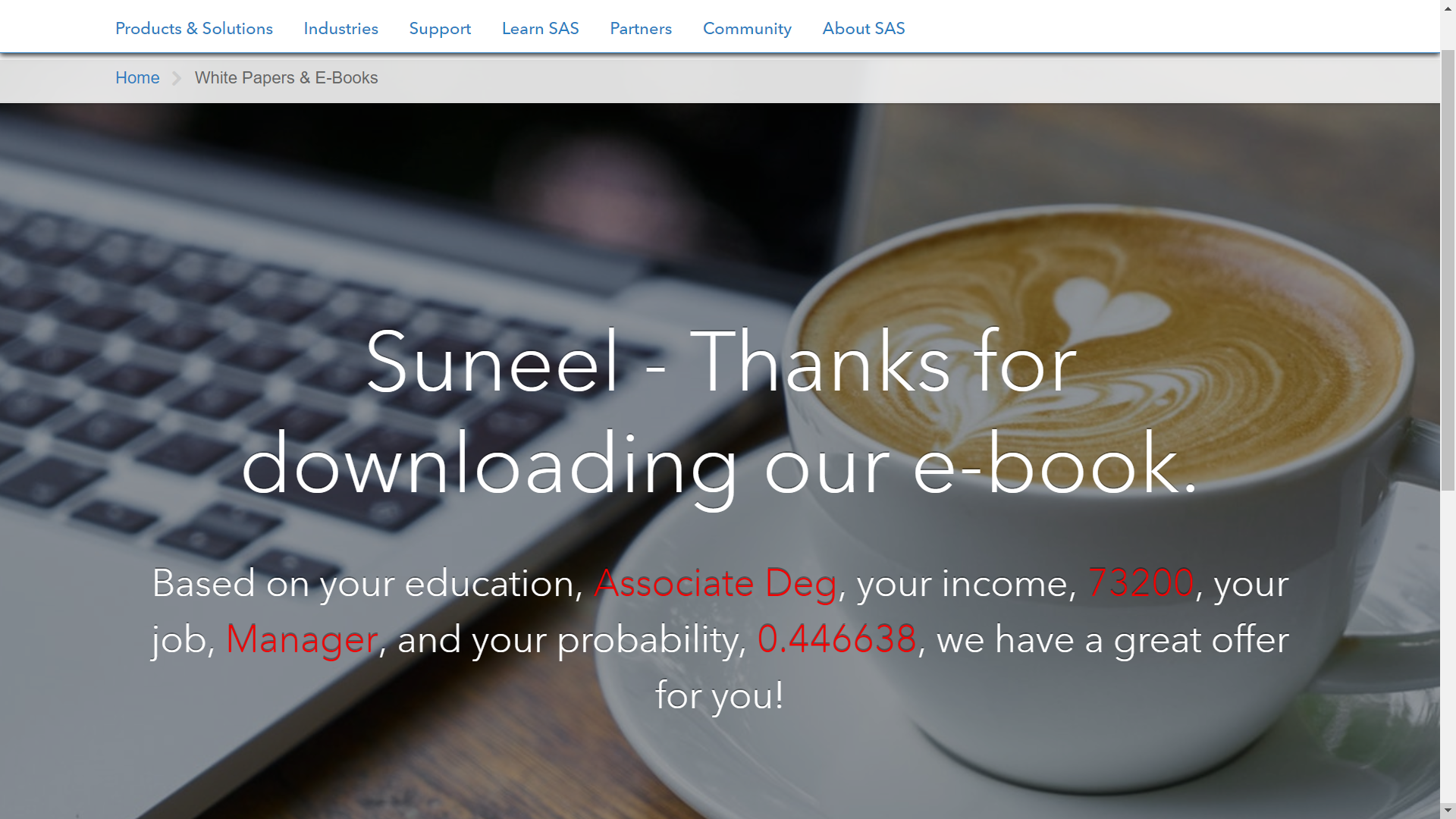
Figure 15 shows what this could look like in reality for the customer (although I’m not suggesting you show your customers the parameters that drive your targeting strategy). How your organization chooses to customize the experience and offer is based on your creative imagination. Examples range from unique call-to-actions, pricing, creative usage, or offer types by segment. My sole purpose here was to inspire your creativity, and highlight how data, analytics, business rules, and creative strategies can morph into one common cause.
SAS Customer Intelligence 360 enables brands to use data to make intelligent decisions using predictive analytics and machine learning in conjunction with business rules across a hub of channel touch points. To learn more about the technology across a variety of use cases, please check out additional posts here.

1 Comment
Pingback: SAS Customer Intelligence 360: Hybrid marketing and analytic's last mile [Part 1] - Customer Intelligence Blog