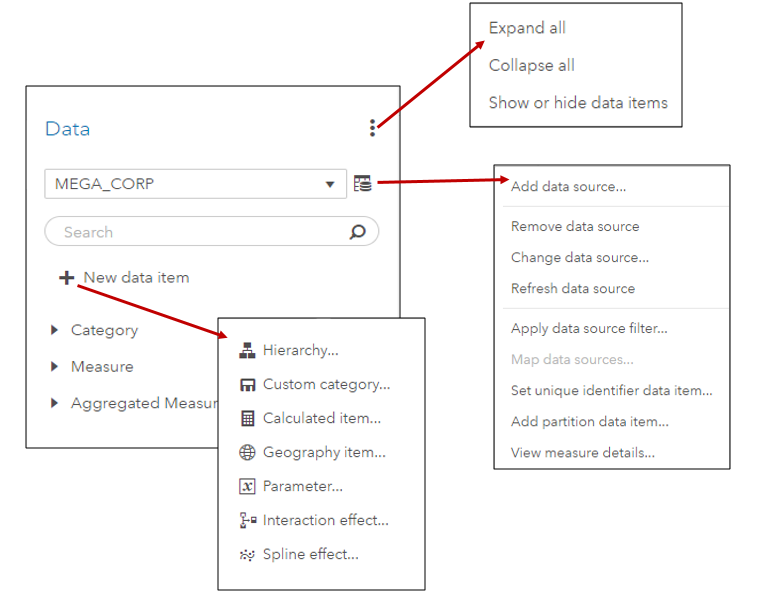
In SAS Visual Analytics 8.2 on Viya 3.3, there are a number of new data features available. I’ll cover a few of these new features including the new data plan and data item features in SAS Visual Analytics in this blog.

In SAS Visual Analytics 8.2 on Viya 3.3, there are a number of new data features available. I’ll cover a few of these new features including the new data plan and data item features in SAS Visual Analytics in this blog.
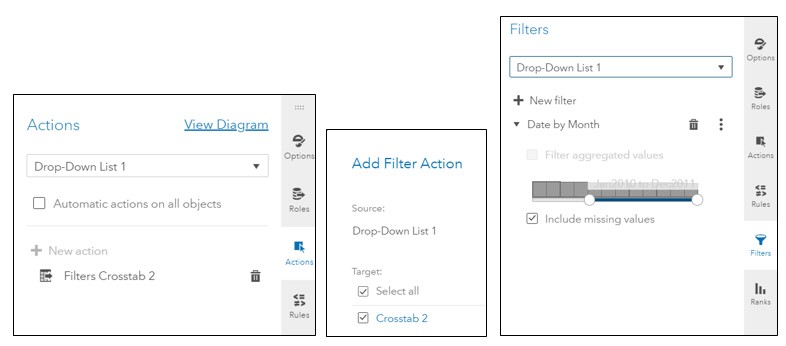
SAS Visual Analytics filters in 7.4 and 8.2 enable you to improve the appearance of reports based on calculations that use periodic operators. Parameter settings also enable you to provide users with a prompt for choosing the data to display in a report, without having any effect on the calculations themselves.
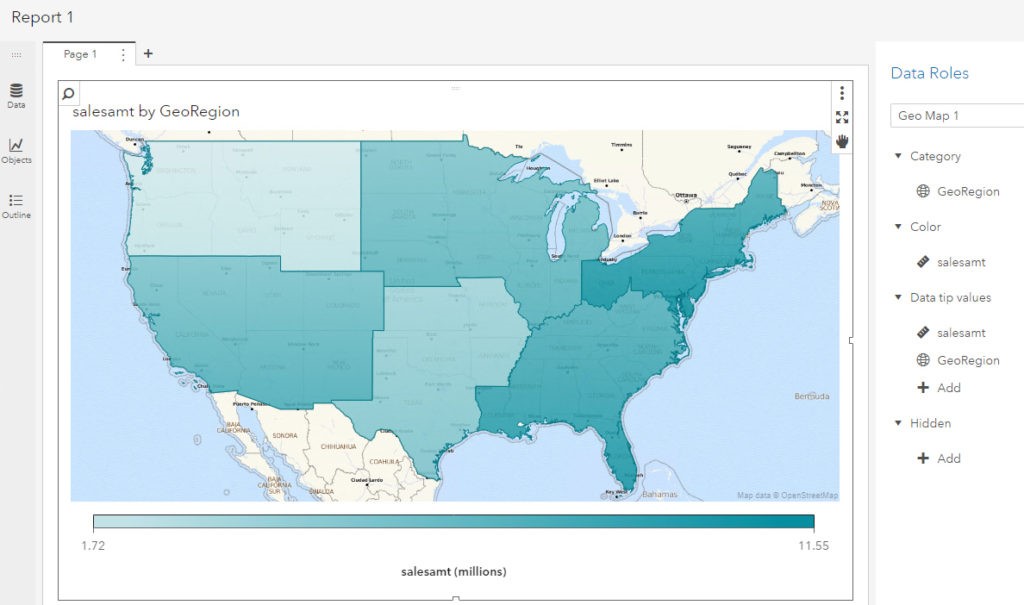
In my last article, I worked with an example of using custom polygon data to create a regional geo map in SAS Visual Analytics 7.4. In this article, I will use almost the same example to illustrate the ease of implementing custom polygons to produce the same regional map in