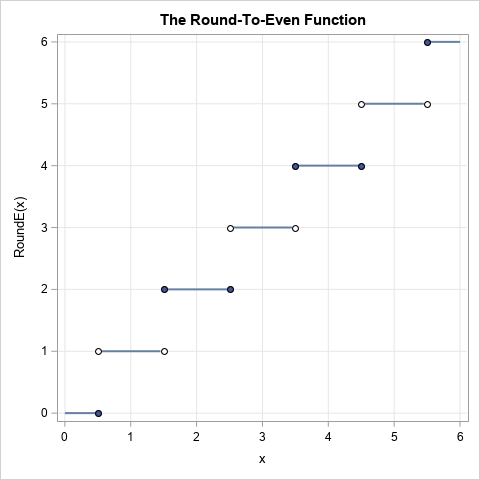
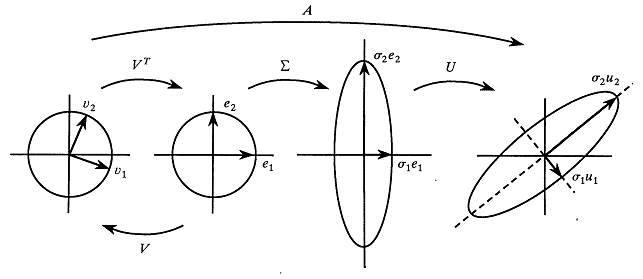
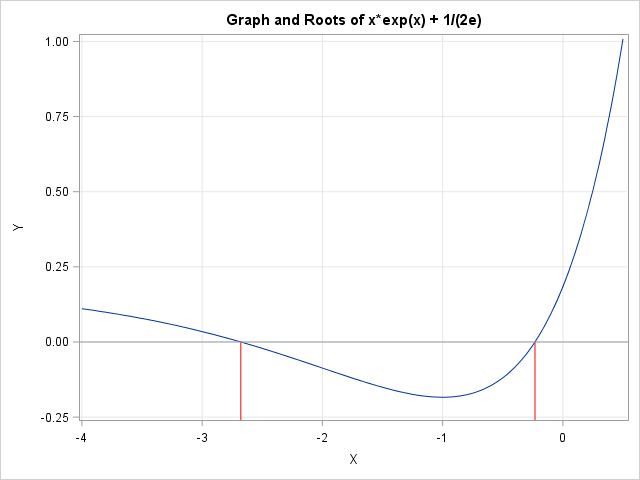
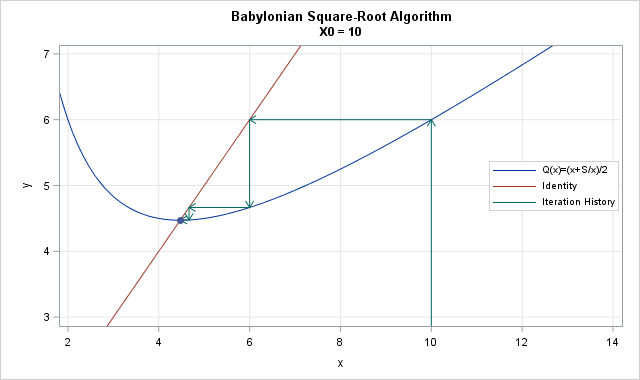
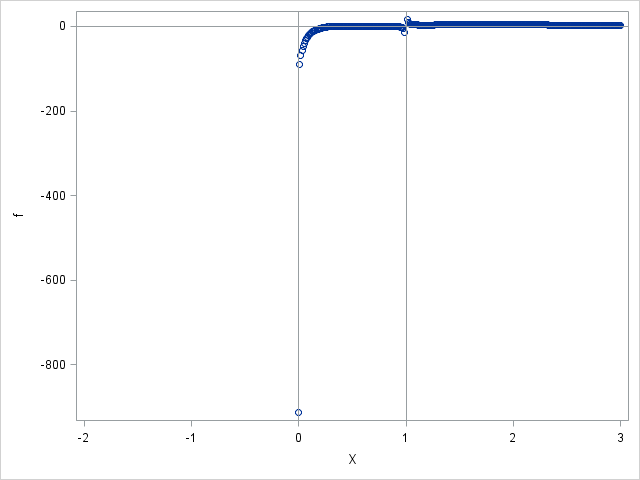
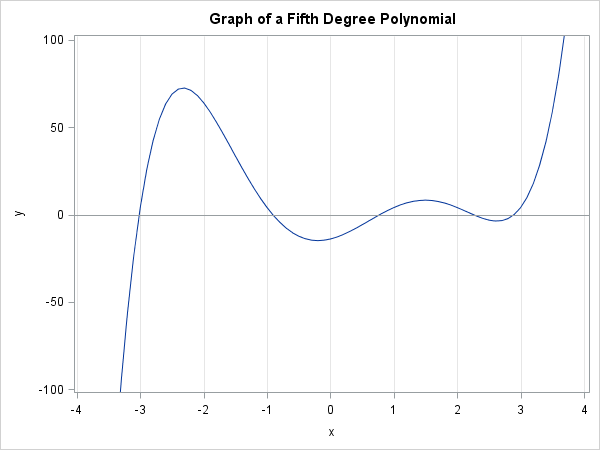
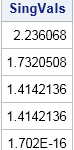
Finite-precision computations can be tricky. You might know, mathematically, that a certain result must be non-negative or must be within a certain interval. However, when you actually compute that result on a computer that uses finite-precision, you might observe that the value is slightly negative or slightly outside of the