The DO Loop
Statistical programming in SAS with an emphasis on SAS/IML programs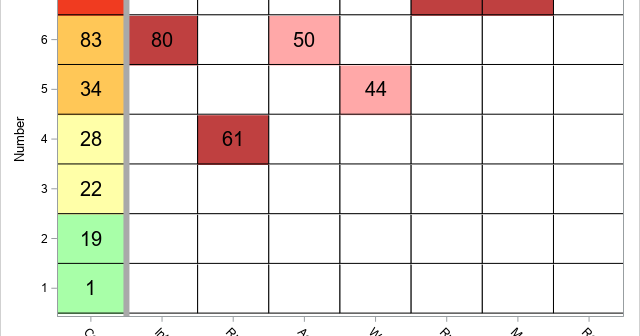
A previous article shows how to interpret the collinearity diagnostics that are produced by PROC REG in SAS. The process involves scanning down numbers in a table in order to find extreme values. This can be a tedious and error-prone process. Friendly and Kwan (2009) compare this task to a
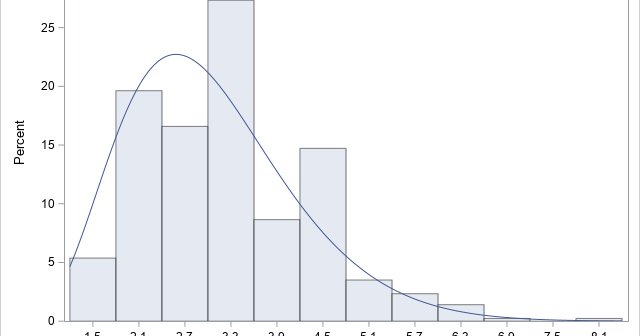
The Johnson system (Johnson, 1949) contains a family of four distributions: the normal distribution, the lognormal distribution, the SB distribution, and the SU distribution. Previous articles explain why the Johnson system is useful and show how to use PROC UNIVARIATE in SAS to estimate parameters for the Johnson SB distribution
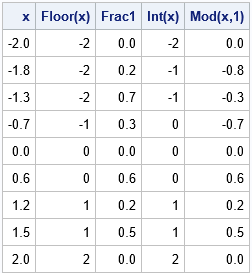
You can represent every number as a nearby integer plus a decimal. For example, 1.3 = 1 + 0.3. The integer is called the integer part of x, whereas the decimal is called the fractional part of x (or sometimes the decimal part of x). This representation is not unique.
