The DO Loop
Statistical programming in SAS with an emphasis on SAS/IML programs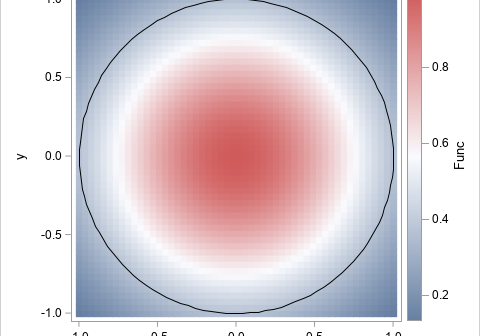
As mentioned in my article about Monte Carlo estimate of (one-dimensional) integrals, one of the advantages of Monte Carlo integration is that you can perform multivariate integrals on complicated regions. This article demonstrates how to use SAS to obtain a Monte Carlo estimate of a double integral over rectangular and
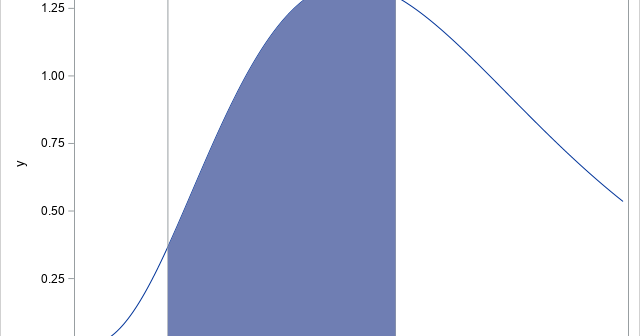
A previous article shows how to use Monte Carlo simulation to estimate a one-dimensional integral on a finite interval. A larger random sample will (on average) result in an estimate that is closer to the true value of the integral than a smaller sample. This article shows how you can

Numerical integration is important in many areas of applied mathematics and statistics. For one-dimensional integrals on the interval (a, b), SAS software provides two important tools for numerical integration: For common univariate probability distributions, you can use the CDF function to integrate the density, thus obtaining the probability that a
