The DO Loop
Statistical programming in SAS with an emphasis on SAS/IML programs
This article uses simulation to demonstrate the fact that any continuous distribution can be transformed into the uniform distribution on (0,1). The function that performs this transformation is a familiar one: it is the cumulative distribution function (CDF). A continuous CDF is defined as an integral, so the transformation is
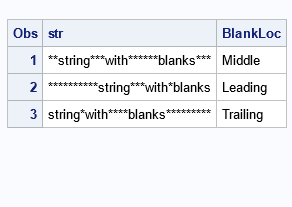
A SAS programmer noticed that his SAS output was not displaying multiple blanks in his strings. He had some strings with leading blanks, others with trailing blanks, and others with multiple blanks in the middle. Yet, every time he used SAS to print the strings to the HTML destination, something
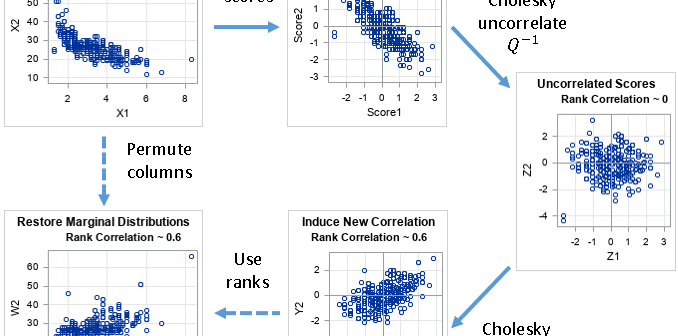
A previous article showed how to simulate multivariate correlated data by using the Iman-Conover transformation (Iman and Conover, 1982). The transformation preserves the marginal distributions of the original data but permutes the values (columnwise) to induce a new correlation among the variables. When I first read about the Iman-Conover transformation,
