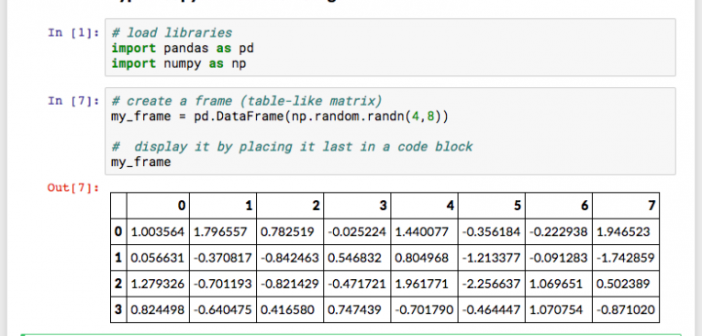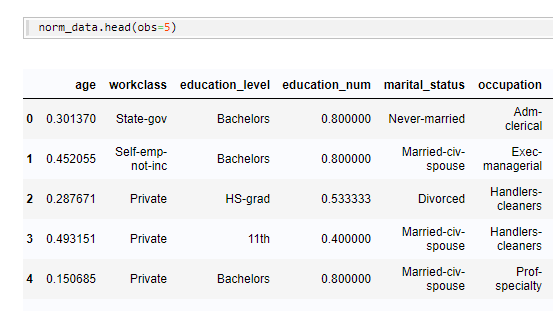
Parts 1 and 2 of this blog post discussed exploring and preparing your data using SASPy. To recap, Part 1 discussed how to explore data using the SASPy interface with Python. Part 2 continued with an explanation of how to prepare your data to use it with a machine-learning model.