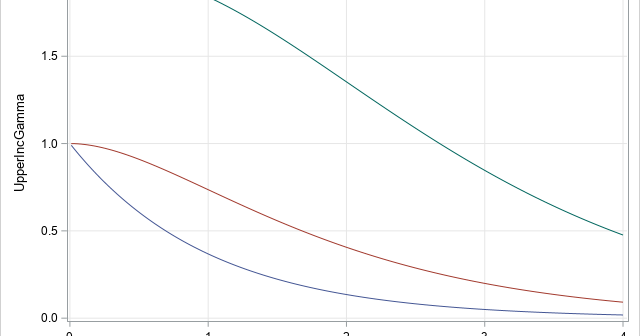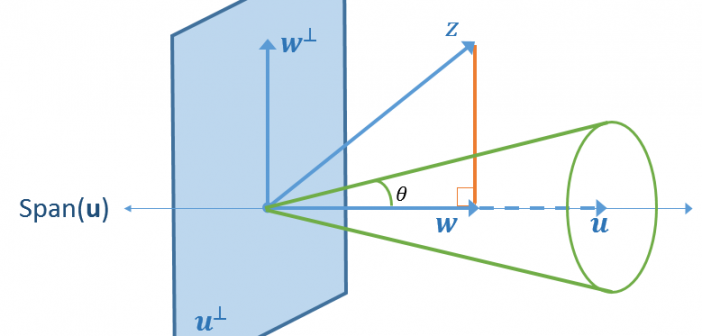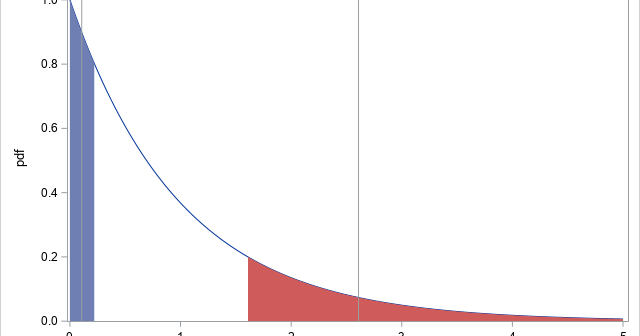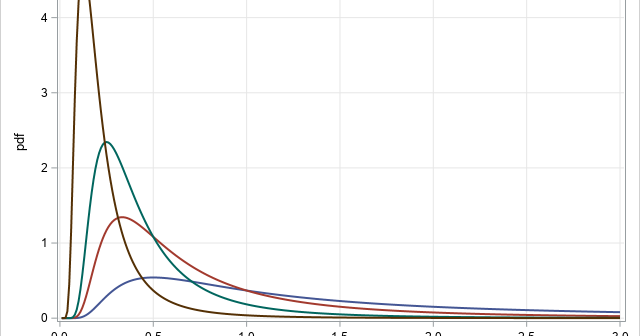
The inverse gamma distribution is a continuous probability distribution that is used in Bayesian analysis and in some statistical models. The inverse gamma distribution is closely related to the gamma distribution. For any probability distribution, it is essential to know how to compute four functions: the PDF function, which returns