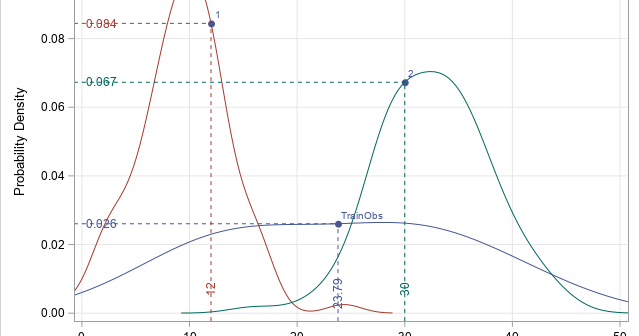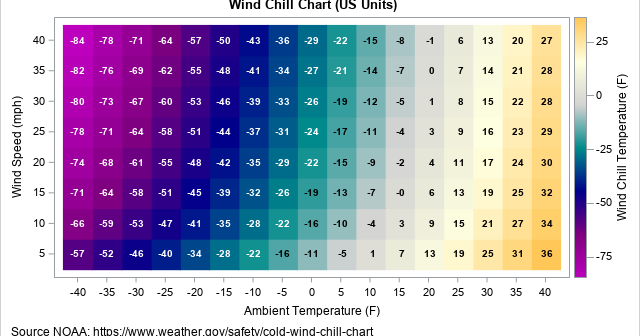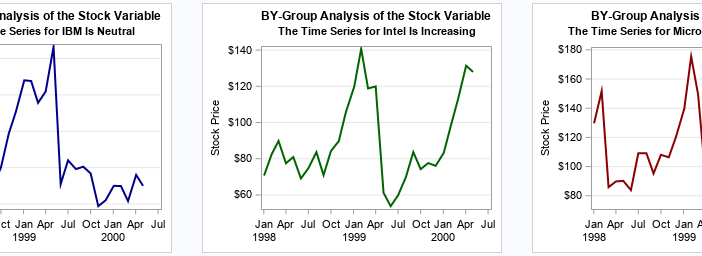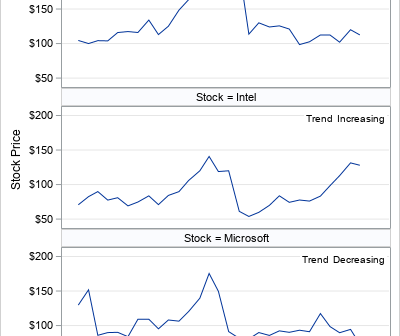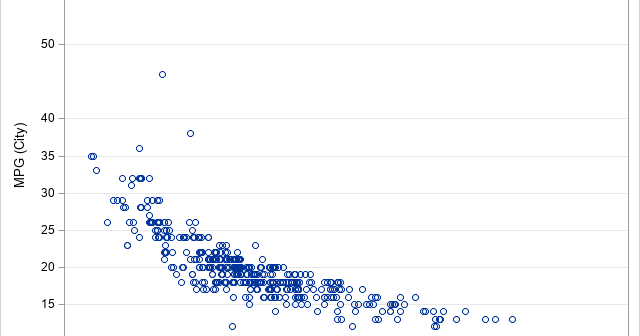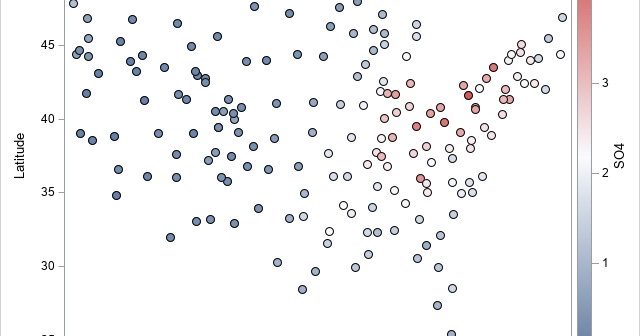
This article shows how to use PROC SGPLOT in SAS to create the scatter plot shown to the right. The scatter plot has the following features: The colors of markers are determined by the value of a third variable. The outline of each marker is the same color (such as