The DO Loop
Statistical programming in SAS with an emphasis on SAS/IML programs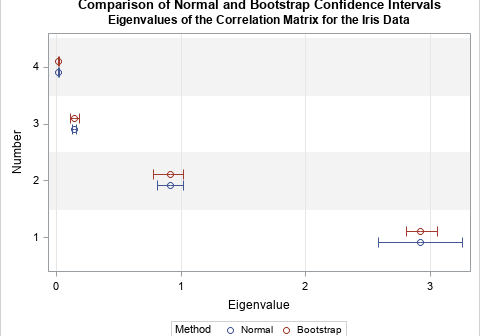
A fundamental principle of data analysis is that a statistic is an estimate of a parameter for the population. A statistic is calculated from a random sample. This leads to uncertainty in the estimate: a different random sample would have produced a different statistic. To quantify the uncertainty, SAS procedures
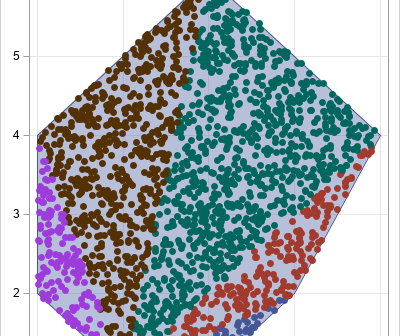
The triangulation theorem for polygons says that every simple polygon can be triangulated. In fact, if the polygon has V vertices, you can decompose it into V-2 non-overlapping triangles. In this article, a "polygon" always means a simple polygon. Also, a "random point" means one that is drawn at random
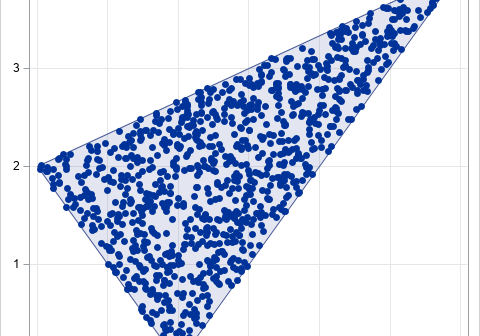
How can you efficiently generate N random uniform points in a triangular region of the plane? There is a very cool algorithm (which I call the reflection method) that makes the process easy. I no longer remember where I saw this algorithm, but it is different from the "weighted average"
