The DO Loop
Statistical programming in SAS with an emphasis on SAS/IML programs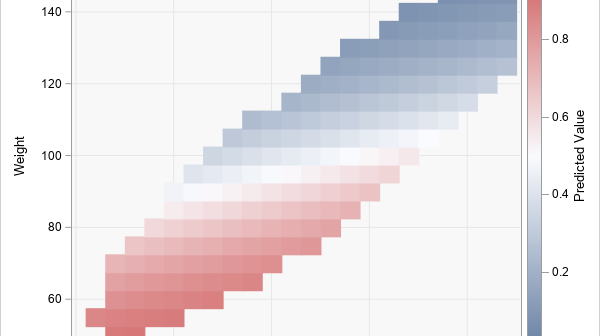
To help visualize regression models, SAS provides the EFFECTPLOT statement in several regression procedures and in PROC PLM, which is a general-purpose procedure for post-fitting analysis of linear models. When scoring and visualizing a model, it is important to use reasonable combinations of the explanatory variables for the visualization. When
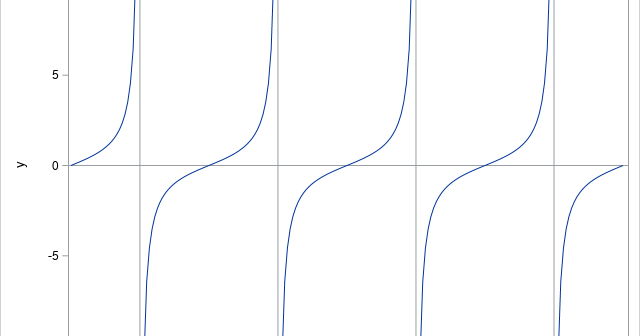
I have previously written about how to plot a discontinuous function in SAS. That article shows how to use the GROUP= option on the SERIES statement to graph a discontinuous function. An alternative approach is to place a missing value for the Y variable at the locations at which the
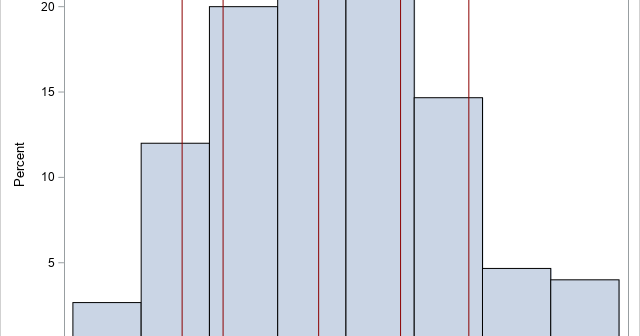
The REFLINE statement in PROC SGPLOT is one of my favorite ways to augment statistical graphics such as scatter plots, series plots, and histograms. The REFLINE statement overlays a vertical or horizontal reference line on a graph. You can specify the location of the reference lines on the REFLINE statement.
