The DO Loop
Statistical programming in SAS with an emphasis on SAS/IML programs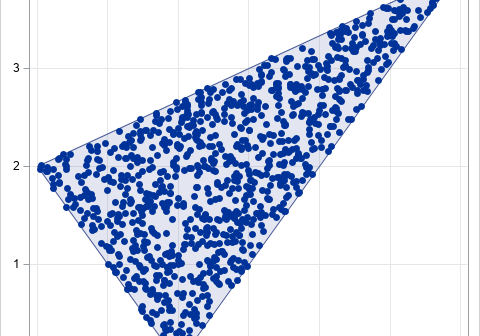
How can you efficiently generate N random uniform points in a triangular region of the plane? There is a very cool algorithm (which I call the reflection method) that makes the process easy. I no longer remember where I saw this algorithm, but it is different from the "weighted average"
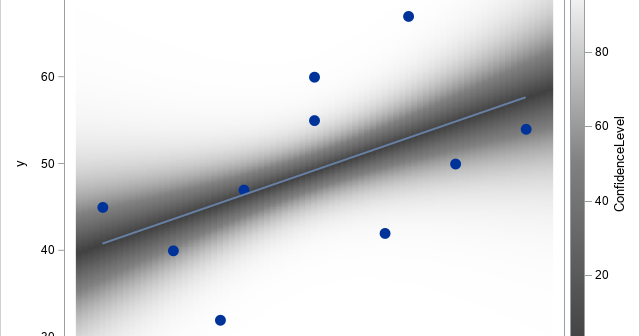
A previous article discusses the confidence band for the mean predicted value in a regression model. The article shows a "graded confidence band plot," which I saw in Claus O. Wilke's online book, Fundamentals of Data Visualization (Section 16.3). It communicates uncertainty in the predictions. A graded band plot is
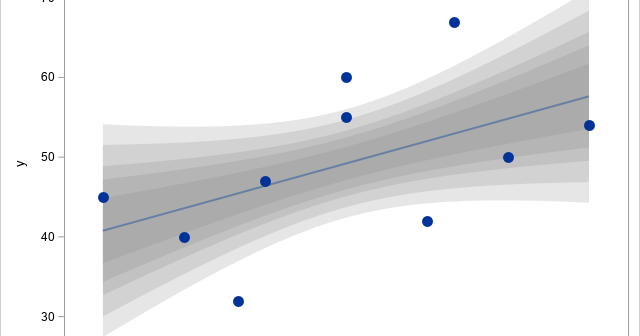
You've probably seen many graphs that are similar to the one at the right. This plot shows a regression line overlaid on a scatter plot of some data. Given a value for the independent variable (x), the regression line gives the best prediction for the mean of the response variable
