The DO Loop
Statistical programming in SAS with an emphasis on SAS/IML programs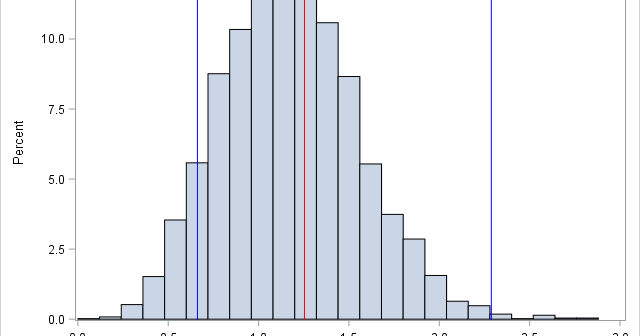
I recently showed how to compute a bootstrap percentile confidence interval in SAS. The percentile interval is a simple "first-order" interval that is formed from quantiles of the bootstrap distribution. However, it has two limitations. First, it does not use the estimate for the original data; it is based only
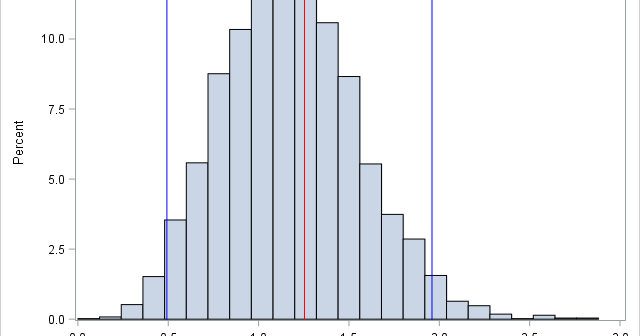
I previously wrote about how to compute a bootstrap confidence interval in Base SAS. As a reminder, the bootstrap method consists of the following steps: Compute the statistic of interest for the original data Resample B times from the data to form B bootstrap samples. B is usually a large

A SAS customer asked how to use SAS to conduct a Z test for the equality of two proportions. He was directed to the SAS Usage Note "Testing the equality of two or more proportions from independent samples." The note says to "specify the CHISQ option in the TABLES statement
