The most recent development environment for SAS programmers is SAS Studio, which is a browser-based application. The free SAS University Edition, which includes SAS/IML software, also uses SAS Studio as a development environment. SAS Studio has a special mode for programmers who use interactive procedures such as PROC IML. (Recall
Tag: SAS Programming
Last week my colleague Chris Hemedinger published a blog post that described how to use the ODS LAYOUT GRIDDED statement to arrange tables and graphs in a panel. The statement was introduced in SAS 9.4m1 (December 2013). Gridded layout is supported for HTML, POWERPOINT, and the PRINTER family of destinations
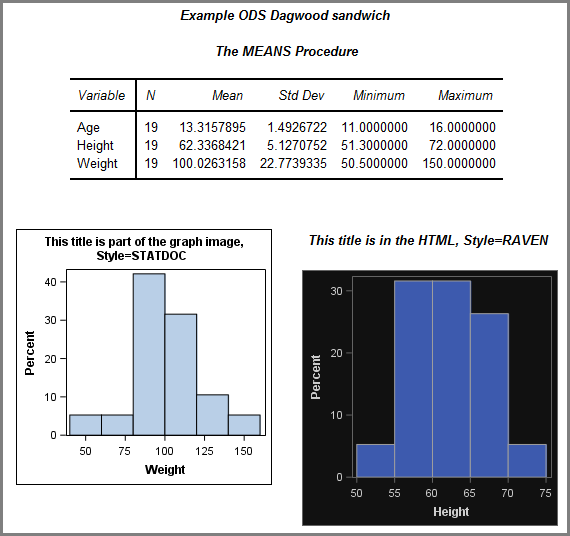
The ODS statement controls most aspects of how SAS creates your output results. You use it to specify the destination type (HTML, PDF, RTF, EXCEL or something else), as well as the details of those destinations: file paths, appearance styles, graphics behaviors, and more. The most common use pattern is
Sometimes you are writing a program that needs to find out whether a particular SAS product (like SAS/ETS, SAS/QC, or SAS/OR) is licensed. I was reminded of this fact when I wrote last week's blog post about how to create a map with PROC SGPLOT. Although the SGPLOT procedure is
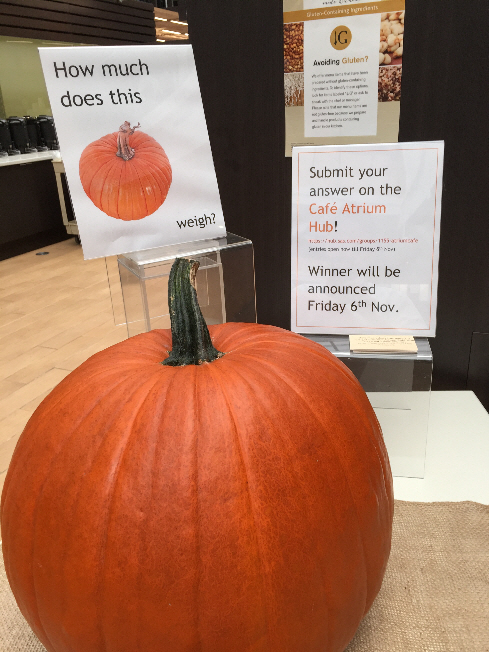

How much does this big pumpkin weigh? One of the cafeterias at SAS invited patrons to post their guesses on an internal social network at SAS. There was no prize for the correct guess; it was just a fun Halloween-week activity. I recognized this as an opportunity to apply the
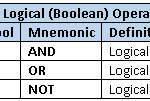
In SAS, the DATA step and PROC SQL support mnemonic logical operators. The Boolean operators AND, OR, and NOT are used for evaluating logical expressions. The comparison operators are EQ (equal), NE (not equal), GT (greater than), LT (less than), GE (greater than or equal), and LE (less than or

I've previously written about how to generate a sequence of evenly spaced points in an interval. Evenly spaced data is useful for scoring a regression model on an interval. In the previous articles the endpoints of the interval were hard-coded. However, it is common to want to evaluate a function

Statistical programmers often have to use the results from one SAS procedure as the input to another SAS procedure. Because ODS enables you to you to create a SAS data set from any ODS table or graph, it is easy to obtain a data set that contains the value of

Our new book, Exercises and Projects for The Little SAS® Book Fifth Edition, includes a variety of exercises to help people learn SAS programming. Rebecca Ottesen, Lora Delwiche and I designed this book so that it can be used either in a classroom setting or by individual readers working alone.
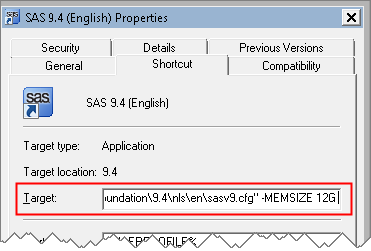
Last week, SAS released the 14.1 version of its analytics products, which are shipped as part of the third maintenance release of 9.4. If you run SAS/IML programs from a 64-bit Windows PC, you might be interested to know that you can now create matrices with about 231 ≈ 2
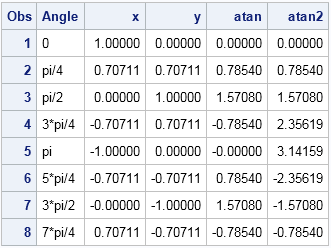
Equations that involve trigonometric functions can have infinitely many solutions. For example, the solution to the equation tan(θ)=1 is θ = π/4 + kπ, where k is any integer. In order to obtain a unique solution to the equation, we define the "arc" functions: inverse trigonometric functions that return a

When reading a text file (common extensions: TXT, DAT; or, for the adventurous: HTML) with the DATA STEP, you should always view several lines from the text file, and compare to the record layout, before completing the INPUT statement. There are many ways to view a text file. I use

I previously wrote about the best way to suppress output from SAS procedures. Suppressing output is necessary in simulation and bootstrap analyses, and it is useful in other contexts as well. In my previous article, I wrote, "many programmers use ODS _ALL_ CLOSE as a way to suppress output, but

Dataset too big for PROC PRINT? One weird trick solves your problem! proc print data=bigdata (obs=10); run; The OBS= dataset option specifies the last observation to process from an input dataset. In the above example, regardless of dataset size, only the first 10 observations are printed; an easy way to

Many of our authors often ask us where they can find real data that they can use without copyright or other confidentiality issues. Instructors too are always on the look-out for real-life data. Well, thanks to a new initiative supported by SAS, you can now access data from more than

New York City Mayor, Michael Bloomberg made a new-year's resolution to learn code. Apple’s Steve Jobs said, “I think everybody in this country should learn how to program a computer because it teaches you how to think.” President Barrack Obama said, "Don't just buy a new video game, make one.

I watched with wonder as each of my daughters learned how to "tell time." Early in their primary school careers, they brought home worksheets that featured clock faces with big-hand/little-hand configurations that they had to decipher, and exercises that asked them to draw the hands as they should appear given

So, how did you first learn SAS programming? Originally, I was self-taught. Many years ago, I learned SAS on the job when a systems programmer quit and I took over supporting a mainframe performance software package that was written in SAS. I got a copy of the Base SAS users
Most SAS programmers have been here. Someone just wants a handful of numbers that they can add to a graph or power point presentation that is due tomorrow. You have the data files, you have a job to summarize it, and you have a dilemma. How do I get my
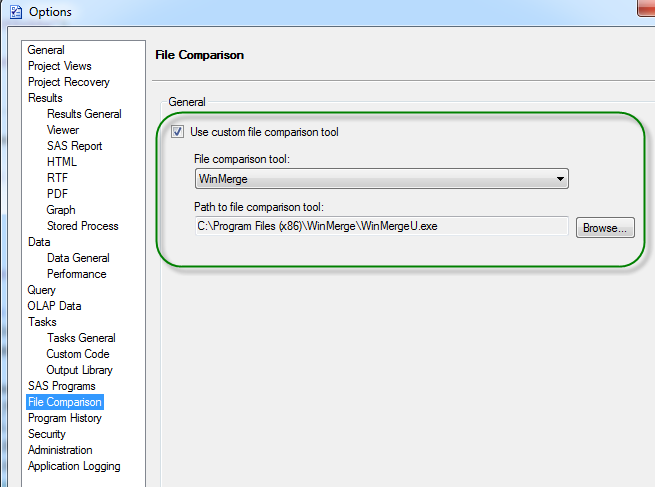
Copy/paste is my favorite method for creating new SAS programs. In my work projects, I maintain a sort of genealogy of SAS programs, because the DNA of one program can be used to spawn many other SAS programs as its progeny. When things (inevitably) aren't working as I intend in
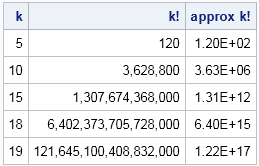
There's "big," and then there is "factorial big." If you have k items, the number of permutations is "k factorial," which is written as k!. The factorial function gets big fast. For example, the value of k! for several values of k is shown in the following table. You can
With any software program, there are always new tips and tricks to learn, and nobody can know them all. Sometimes I even pick up tips or techniques from my students while they’re learning broader programming tips from me. Like fine wine, instructors only get better with age. Every customer interaction
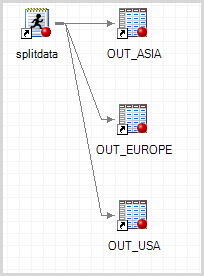
This article show how to run a SAS program in batch mode and send parameters into the program by specifying the parameters when you run SAS from a command line interface. This technique has many uses, one of which is to split a long-running SAS computation into a series of

SAS Global Forum brings together the most die-hard SAS users, both veteran and novice, once a year. It’s one of those can’t-miss events, and each year it just gets better. 2015 will bring us all together in Dallas, Texas for several days of active learning and excitement from SAS users
Back in the day when the prison system forced inmates to perform "hard labor", folks would say (of someone in prison): "He's busy making little ones out of big ones." This evokes the cliché image of inmates who are chained together, forced to swing a chisel to break large rocks
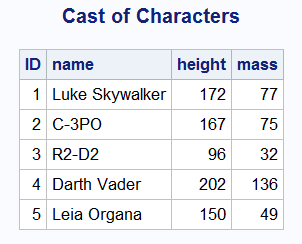
While perusing the SAS 9.4 DS2 documentation, I ran across the section on the HTTP package. This intrigued me because, as DS2 has no text file handling statements I assumed all hope of leveraging Internet-based APIs was lost. But even a Jedi is wrong now and then! And what better

Last year, 50 companies came knocking on the doors of Rotman School of Management in Canada to recruit Masters of Business Administration (MBA) grads with SAS skills. This year, Rotman partnered with SAS to offer SAS Programming to interested candidates. Last Sunday, I had the amazing opportunity to teach SAS
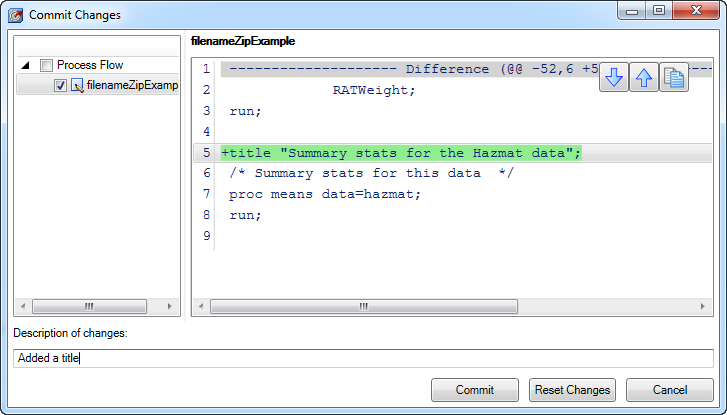
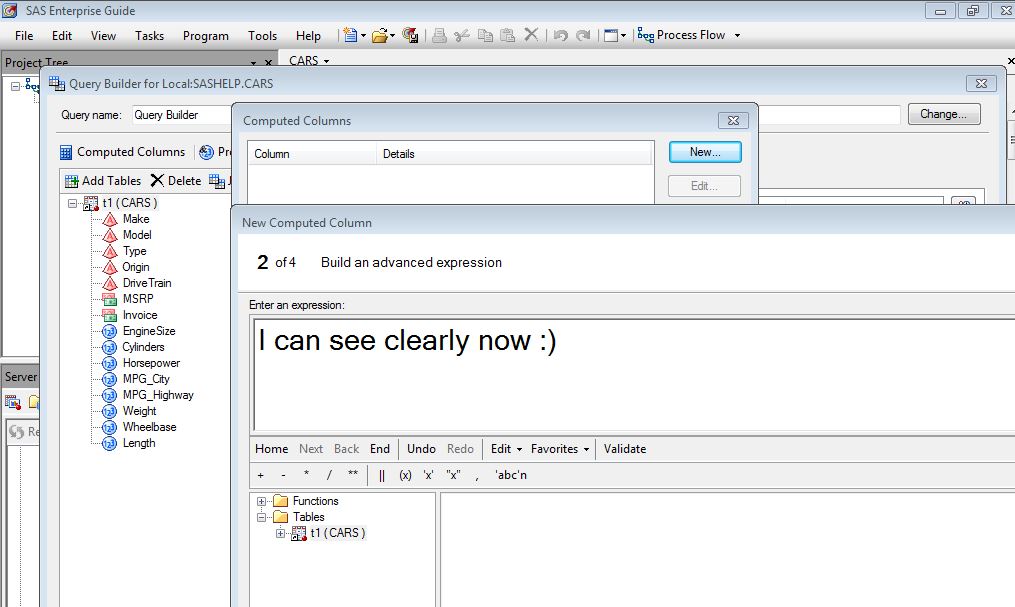
SAS Enterprise Guide 7.1 began shipping last week. Of the many new features, some are "biggies" while others are more subtle. My favorite new features are those for SAS programmers, including several items that I've heard customers ask for specifically. I'll describe them briefly here; the SAS Enterprise Guide online
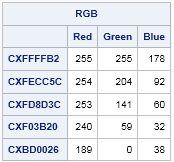
In response to my recent post about how to use the PALETTE function in SAS/IML to generate color ramps, a reader wrote the following: The PALETTE function returns an array of hexadecimal values such as CXF03B20. For those of us who think about colors as RGB values, is there an
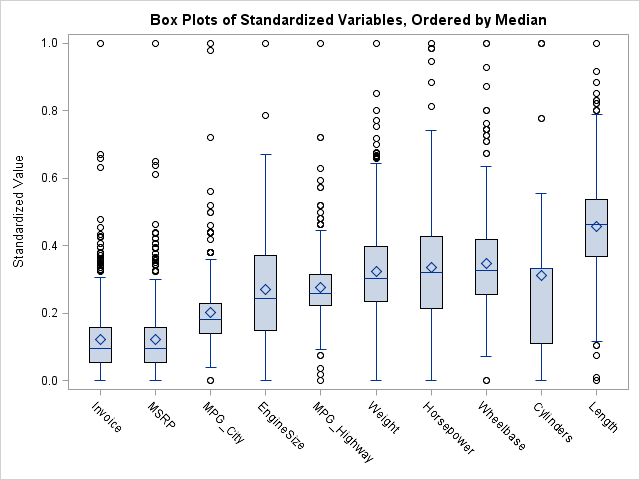
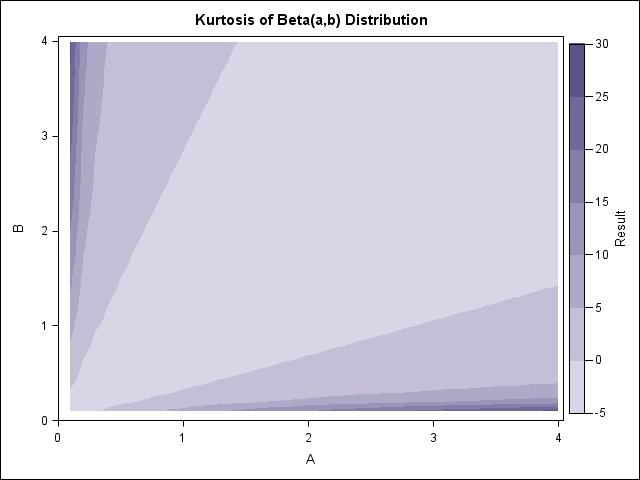
When I create a graph of data that contains a categorical variable, I rarely want to display the categories in alphabetical order. For example, the box plot to the left is a plot of 10 standardized variables where the variables are ordered by their median value. The ordering makes it









