Analytics can get you answers from data. With an ever-increasing volume of data and new regulatory pressures, you need to know more than knowing where and how it is used. It's critical to comprehend the data: Is it relevant? Does it contain sensitive or private information? Can we detect bias? Data scientists are answering questions like these using automation and collaboration to help manage data proliferation and understanding.
However, before you get the answers, you need to know where to find the data and if the data fits your purpose. Traditional metadata solutions focus on understanding how data and processes in a deployment relate to each other and how process changes affect downstream consumers. This automation and collaboration are made possible by metadata. The following vital characteristics can further explain the value of metadata:
1. Metadata can define the schema of stored assets
Metadata must be stored and represented in a flexible and adaptable format. Metadata serves as a critical tool in defining the schema of accumulated assets. It provides information about the characteristics and properties of data, including data type, format, and relationships to other data elements. One key feature of the critical features of SAS® Viya® is the ability to define metadata properties. These metadata properties add valuable information about the data and analytic assets, making it easier for users to find and use them effectively.
2. Metadata can automate data quality and statistics through discovery agents
Automation is necessary to gain comprehensive insights into volumes of data quickly. To that end, discovery agents crawl a library's data, inferring its physical structure and calculating various valuable metrics. Such metrics include descriptive statistics, quantities, distributions and data profiling analysis. The SAS Information Governance license also includes semantic type assignment and information privacy classification. Profiling insights can help assess data quality and be augmented with tagging and scoring.
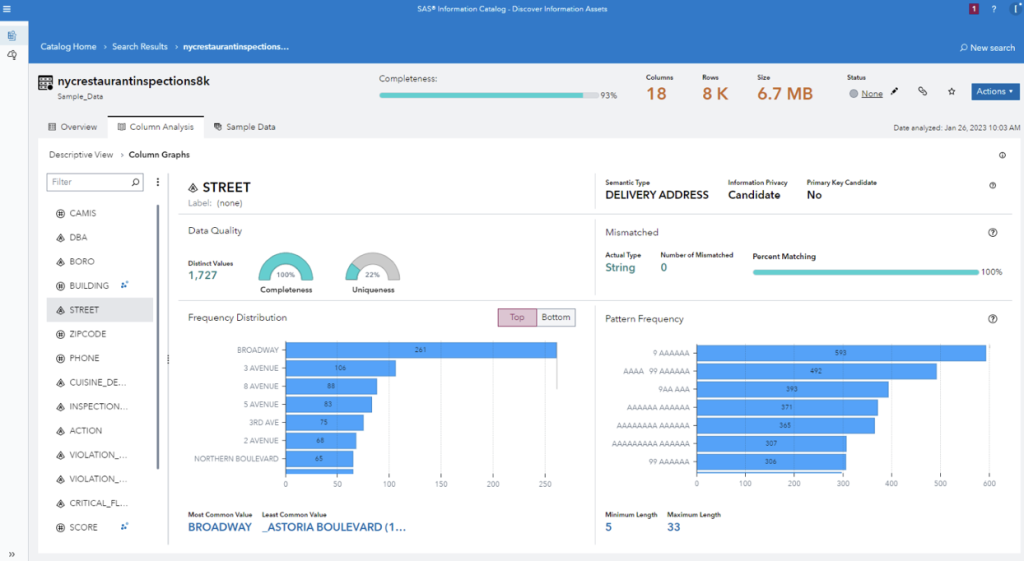
3. Metadata supports knowledge sharing
Knowledge sharing is critical for organizational success in analytics deployment. SAS Information Catalog provides asset knowledge sharing via the subject matter expert role. The subject matter expert can add a business description, a status update and custom tags to any catalog asset. SAS Information Catalog also provides automated summary and topic generation based on the content of data sets. This automation enables a quick evaluation of the contents of unknown data.
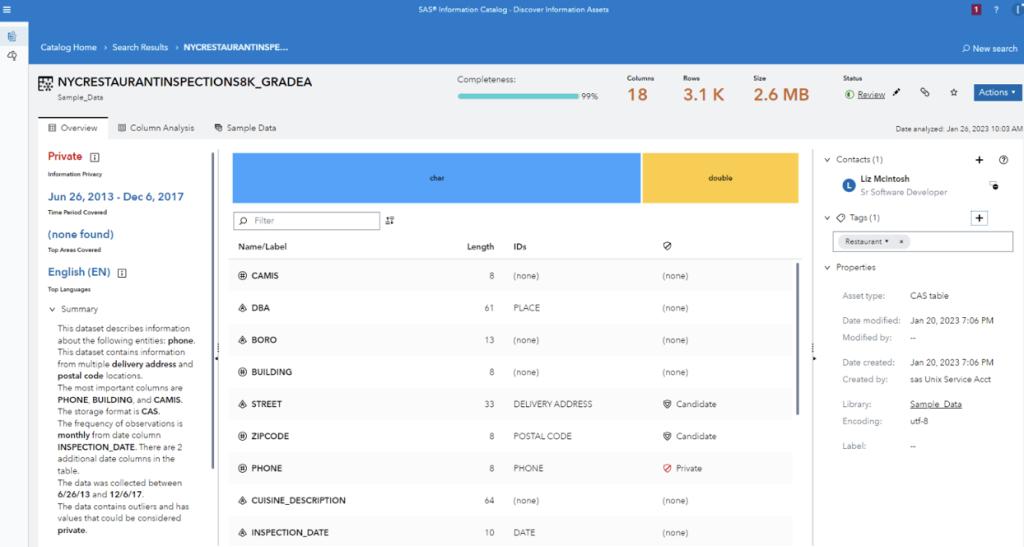
4. Metadata support fast, scalable search
Finding the right data is key when searching for analytic insights. Metadata solutions will combine custom schema, metrics and knowledge sharing in a fast, scalable search. In SAS Viya, metadata about information assets and relationships to data is automatically loaded into SAS Information Catalog. The metadata properties and search capabilities are designed so that no technical knowledge is required to find relevant results. Based on OpenSearch, it is highly scalable and extremely fast.
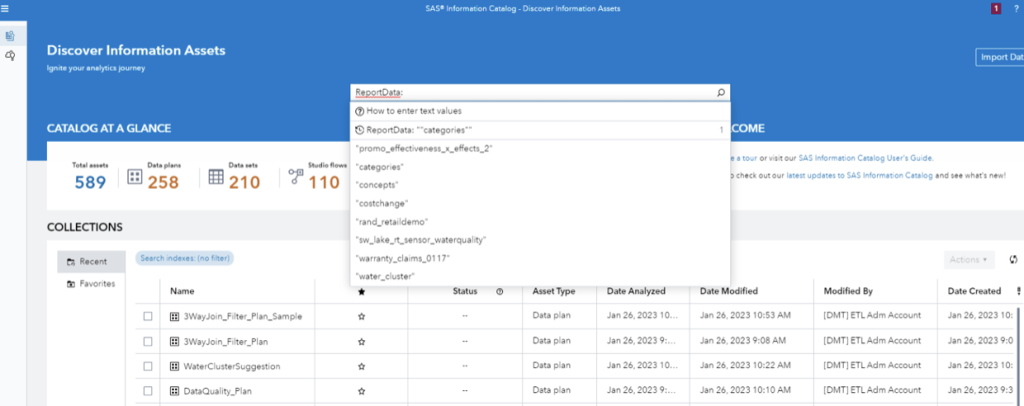
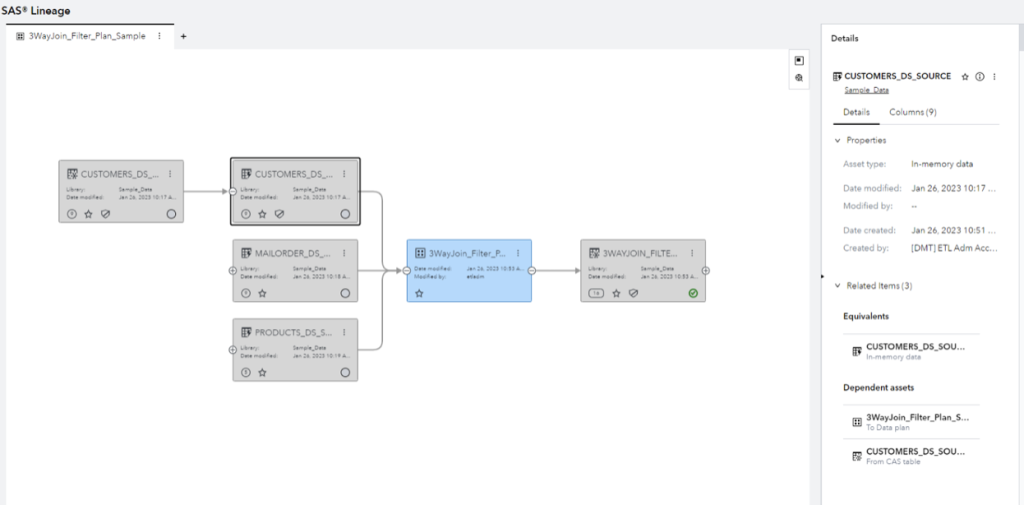
5. Metadata support easy-to-understand data lineage and impact analysis
Understanding where data comes from, how it is transformed, and where it goes is essential to understanding analytic processes. You also need to understand the impact of changes in any part of the process. Metadata enables this understanding by providing data lineage and impact analysis. SAS Lineage provides a graphical interface for clear impact analysis for metadata-described assets. It also displays custom properties and key information are also displayed that answer questions such as whether the data contains sensitive or private information, the data's status and which library loaded the data.
Organizations must use metadata to understand their data better and obtain valuable insights in today's data-driven world. As the volume of data increases, it is important to comprehend the data and ensure its relevance, accuracy and privacy. A metadata solution like SAS Information Catalog enables the discovery of metadata. It provides features enabling users to locate relevant data and determine the fitness of data for the intended use, rather than simply telling them where data is located and used.
By using metadata, organizations can make better-informed decisions, improve data quality and achieve business objectives. That's why metadata is essential for any organization looking for success in the age of big data.

